Difference between revisions of "Gas"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Gases=== | ||
| + | : When a [[substance]] is in its [[gas]]eous [[State of Matter|state]] it is always less [[Density|dense]] than in its [[liquid]] or [[gas]]eous [[State of Matter|state]]. | ||
| + | : A [[substance]] which is [[gas]]eous at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]] has a smaller [[force]] of [[attraction]] between [[particle]]s than a [[substance]] which is [[liquid]] or [[solid]] at [[Room Temperature|room temperature]]. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 18:03, 23 December 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
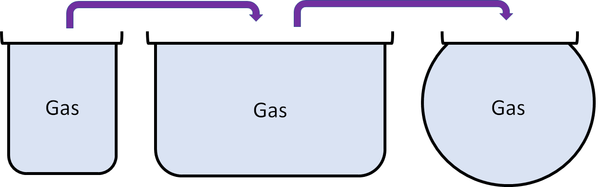
Gas is a state of matter that can change size and shape to fit any container.
About Gases
- Most gases are invisible but we can feel them.
- When the air moves we call it the wind.
|
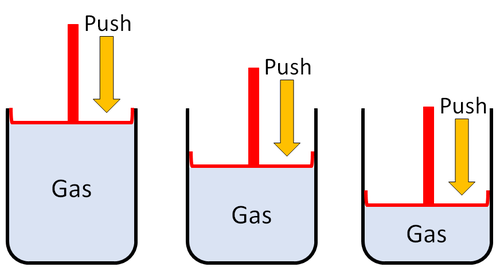
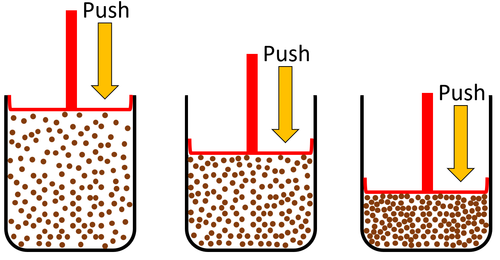
| Gases can be squashed into a smaller size. |
Examples of gas materials:
- Air (A mixture of gases, mostly nitrogen and oxygen)
- Steam
Key Stage 3
Meaning
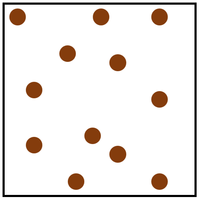
Gas is a State of Matter in which the particles are separated by large distances and can move freely.
About Gases
| Gas can be squashed into a smaller size because the particles are spread apart. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
About Gases
- When a substance is in its gaseous state it is always less dense than in its liquid or gaseous state.
- A substance which is gaseous at room temperature has a smaller force of attraction between particles than a substance which is liquid or solid at room temperature.
| Particle Diagram | Particle Arrangement | Property |
| Particles are free to move in all directions. | Gases fit the size of their container. | |
| Gases fit the shape of their container. | ||
| Convection happens most easily in gases. | ||
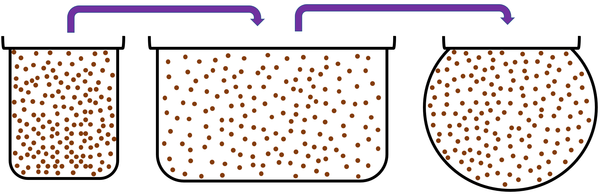
| Particles are spread apart. | Gases can be compressed into a smaller volume. | |
| Sound passes through gases slower than liquids and solids. | ||
| Thermal Conduction is very poor in a gases. |