Carbon Cycle
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The Carbon Cycle is a set of processes that naturally recycle Carbon.
About the Carbon Cycle
- Some processes put Carbon into the atmosphere as Carbon Dioxide and others take Carbon Dioxide out of the atmosphere.
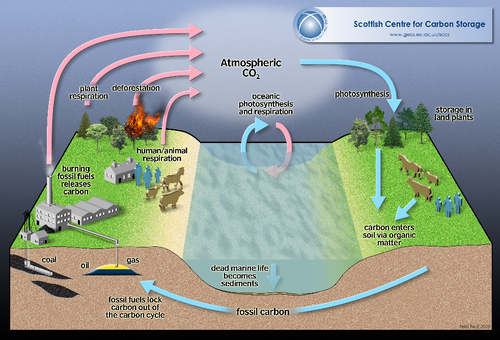
| This diagram shows Carbon Cycle which shows how photosynthesis takes Carbon Dioxide out of the atmosphere. |
Adding Carbon Dioxide to the Atmosphere
- Respiration - All living creatures respire and produce Carbon Dioxide.
- Combustion of Fossil Fuels - When Coal and Crude Oil are burned they produce Carbon Dioxide.
- Decay - When organisms rot or decay the process produces Carbon Dioxide.
- Volcanoes - These release Carbon Dioxide into the atmosphere.
Removing Carbon Dioxide from the Atmosphere
- Photosynthesis - Most Carbon Dioxide is taken out of the atmosphere by algae photosynthesising in the oceans.
- Dissolving in Oceans - The Oceans absorb Carbon Dioxide.
- Making Shells - Sea creatures with hard shells use Carbon Dioxide dissolved in the water.
Carbon Sinks
A Carbon Sink is part of the Earth that absorbs and stores Carbon.
- The Ocean is a Carbon Sink storing a large amount of dissolved Carbon Dioxide.
- The Sea bed is a Carbon Sink where many organisms, that are made of mostly Carbon, fall to the bottom and get trapped in sediment.
- Forests are Carbon Sinks as the trees use photosynthesis to grow.
- Swamps are Carbon Sinks as many plants get stuck under the water and cannot decay. This Carbon eventually becomes Coal trapped underground.
Disrupting the Carbon Cycle
For millions of years the Carbon Cycle has kept the amount of Carbon Dioxide in the atmosphere very stable. Human activities are now affecting the Carbon Cycle.
- Deforestation - Humans are cutting down forests which stops them taking Carbon Dioxide out of the atmosphere.
- Combustion of Fossil Fuels - Since the industrial revolution the Carbon stored underground has been released into the atmosphere.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Carbon Cycle is a set of processes that naturally recycle Carbon.
References
AQA
- Carbon cycle, page 113, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Carbon cycle, page 270, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Carbon cycle, page 331, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Carbon cycle, page 90, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Carbon cycle, pages 258-9, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Carbon cycle, pages 280-283, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Carbon cycle, pages 88, 95-6, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Cycle, carbon, pages 323, 344-5, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Cycle, carbon; water, pages 323, 342-3, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Carbon cycle, page 102, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Carbon cycle, page 71, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Carbon cycle, pages 140-141, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Carbon cycle, pages 198-199, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Carbon cycle, pages 301, 302, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel