Chromosome
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Chromosomes are coils of DNA found in the nucleus.
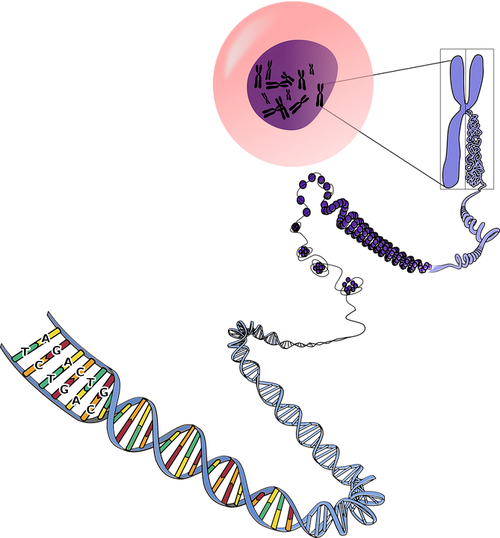
| This diagram shows how DNA is coiled up to make a chromosome. |
About Human Chromosomes
- Humans have 46 chromosomes.
- Chromosomes come in pairs, one from the father and one from the mother.
- 23 chromosomes are from the father and 23 chromosomes are from the mother.
- The last 2 chromosomes are called sex chromosomes and they determine if the offspring is male or female. If the human has two X Chromosomes then they are female. If the human has an X and a Y Chromosome they are male.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A chromosome is a section of DNA that has coiled together.
About Chromosomes
- Chromosomes are found in pairs in diploid cells.
- In organisms which engage in sexual reproduction one of the chromosomes in the pair is inherited from the mother and the other from the father.
- During mitosis chromosomes have made copies of themselves that are joined by a centromere.
- In haploid cells there are half the number of chromosomes. These cells are gametes used in sexual reproduction.
About Human Chromosomes
- Humans have 46 chromosomes.
- 23 chromosomes are from the father and 23 chromosomes are from the mother.
- The last 2 chromosomes' are called sex chromosomes and they determine if the offspring is male or female. If the human has two X Chromosomes then they are female. If the human has an X and a Y Chromosome they are male.
References
AQA
- Chromosome, pages 14, 24-2, 35, 41, 208, 212, 236-9, 240, 242-3, 250-1, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 15, 66, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 15, 84, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 33, 34, 204, 213, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 33, 34, 244, 261, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 34, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 4, 19-20, 27, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 5, 19-20, 27, 183-4, 185, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Chromosomes, pages 6, 8, 26-27, 198-199, 211, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Chromosomes; X and Y, page 69, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Chromosomes; X and Y, page 90, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Chromosomes; X and Y, pages 40-1, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Chromosomes, pages 20, 27, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Chromosomes, pages 24, 34, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Chromosomes, pages 4, 26, 40, 42, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Chromosomes, pages 4, 30, 52, 54, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Chromosomes, pages 58, 89, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Chromosomes; replication, page 41, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Chromosomes; replication, page 53, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Chromosomes; sex chromosomes, page 48, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Chromosomes; sex chromosomes, page 66, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel