Conclusion
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A conclusion is when the results of an experiment are described and explained.
About Conclusions
- A conclusion should describe the results, not just say what the results are. If your results are that 8 people had brown eyes and only 2 has green eyes, that is not a conclusion. You could describe the results by saying 4 times more people have brown eyes than green eyes.
- A conclusion should attempt to explain your results using scientific ideas you understand.
- A conclusion can only be based on the evidence you have and the investigation you performed. If you found most people in your class had brown eyes, that does not mean most people in the world have brown eyes. They may or may not, but you can't use your investigation only looked at your class.
Examples
| Results | Conclusion |
| Descriptive Conclusion
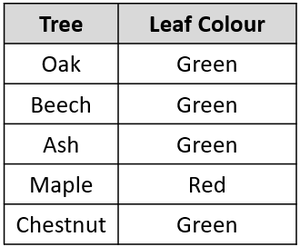
Most trees have green leaves, but not all trees have green leaves because maple has red leaves. | |
| Descriptive Conclusion
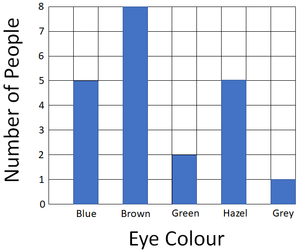
Most people have brown eyes. Grey eyes were the least common. There are the same number of people with blue eyes as hazel eyes. | |
| Explanatory Conclusion
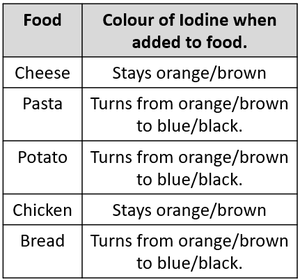
Iodine changes colour when it is in the presence of starch. When the iodine was added to pasta, potato and bread the iodine changed colour from orange/brown to blue/black because they all contain starch. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A conclusion is an attempt to describe and explain the results of an experiment or investigation.
About Conclusions
- A conclusion should describe the results, not just repeat the results in words. If your results are that 8 people had brown eyes and only 2 has green eyes, that is not a conclusion. A conclusion would be to describe the results by saying 4 times more people have brown eyes than green eyes.
- A conclusion should attempt to explain the results using scientific ideas.
- A conclusion can only be based on the evidence from the investigation or experiment performed.
If you found most people in your class had brown eyes, that does not mean most people in the world have brown eyes. They may or may not, but you can't use your investigation only looked at your class.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A conclusion is an attempt to describe and explain the results of an experiment or investigation.
About Conclusions
- A conclusion should describe the results, not just repeat the results in words.
- A conclusion should attempt to explain the results using scientific ideas.
- A conclusion must be valid which means it can only be based on the evidence from the investigation or experiment performed.
References
AQA
- Conclusions, page 10, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 19, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 20, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 21, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 21, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 9, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 9, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, page 9, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, pages 20, 21, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, pages 20-21, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Conclusions, pages 268-269, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Conclusions, pages 281-283, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
Edexcel
- Conclusions, page 10, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Conclusions, page 10, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Conclusions, page 20, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Conclusions, page 9, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Conclusions, pages 20, 21, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Conclusions, pages 21, 22, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel