Coronary Heart Disease
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
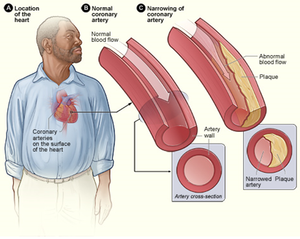
Coronary Heart Disease is a non-communicable disease in which the arteries that supply the heart with oxygen become narrower because of the build up of cholesterol plaques.
About Coronary Heart Disease
- Coronary Heart Disease can lead to a heart attack.
- A Cholesterol plaque is a lump of fat.
Risk Factors in Coronary Heart Disease
- Obesity and a diet high in fat can increase the risk of Coronary Heart Disease.
- Smoking can increase the risk of Coronary Heart Disease.
- Lack of exercise can increase the risk of Coronary Heart Disease.
Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
- In a Coronary Bypass an artery from another part of the body is cut out and attached to the Coronary Artery to provide a path for blood to flow around the blockage.
- A Stent is a tube which can be placed inside the narrow artery and then expanded to widen the artery. The Stent is left inside the artery to hold it open.
Extra Information
References
AQA
- Coronary heart disease, page 103, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Coronary heart disease, page 33, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Coronary heart disease, page 37, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Coronary heart disease, page 97, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Coronary heart disease, pages 56-57, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Coronary heart disease, pages 56-7, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Coronary heart disease, pages 56-8, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA