Diffraction
Key Stage 5

The diffraction pattern produced on a screen when monochromatic light passes through a circular hole.
Meaning
Diffraction is the spreading of waves when they pass through a gap or around an obstacle.
About Diffraction
- Diffraction occurs with all types of waves, including light, sound, and water waves.
- Diffraction is evidence for the wave-like behaviour of matter.
- The extent of diffraction depends on the wavelength of the wave and the size of the gap or obstacle.
- Diffraction is most noticeable when the gap size is comparable to the wavelength.
- Diffraction explains phenomena such as the bending of light around corners and the formation of diffraction patterns.
- Diffraction is used in various applications, including X-ray diffraction to determine crystal structures and electron diffraction to study the properties of materials.
Depictions of Diffraction
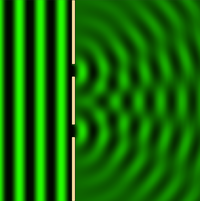
| This image shows a plan view of diffraction of a wave through a single slit. To explore this yourself using physics simulations, visit the website 'phet' by clicking on the image. | This image shows a plan view of diffraction of a wave through a double slit. To explore this yourself using physics simulations, visit the website 'phet' by clicking on the image. |
Examples
- Diffraction patterns are observed when light passes through a single slit.
- Diffraction of sound waves allows us to hear around corners.