Diffuse Reflection
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Reflection is when light bounces off an object and goes into our eyes.
About Reflection
- To see an object light must come from the object and go into our eyes. Most objects do not make their own light, so instead they reflect the light that is made by something else, like The Sun or a light bulb.
- In a dark room you cannot see any objects because there is no light to reflect off the objects.
- When you turn on a light bulb in a dark room the light travels from the light bulb to the objects in the room. The light then reflects off the objects and goes into your eyes. That is how we can see the objects.
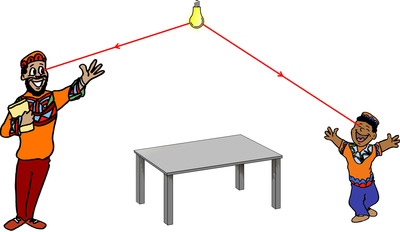
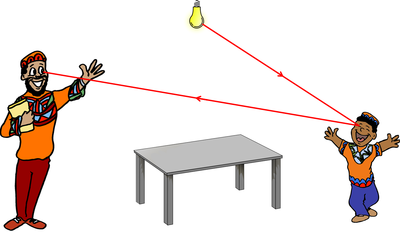
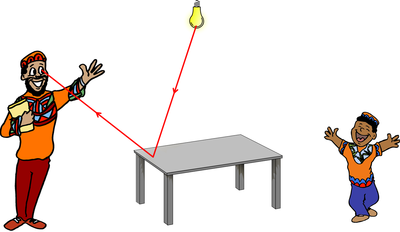
| No-one can see because there is no light to be reflected off anything. | The man can see the light bulb because light from the bulb goes into the man's eyes. The boy cannot see the light bulb because his eyes are closed. |
| The man can see the boy because light from the bulb is reflected off the boy and goes into the man's eyes. | The man can see the table because light from the bulb reflects off the table and goes into the man's eyes. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Diffuse Reflection is when light bounces off a dull surface in different directions.
About Diffuse Reflection
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface that has many tiny bumps and dips.
- Diffuse Reflection is how we see all objects.
- Diffuse Reflection does not produce an image.
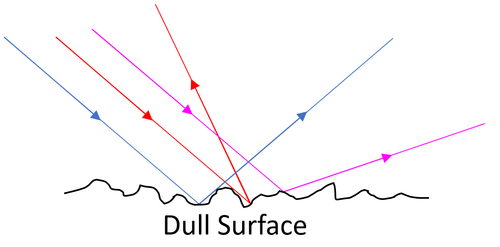
| Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. Parallel incoming rays are reflected in different directions. This known as scattering. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Diffuse Reflection is when an Electromagnetic Wave bounces off the interface between a transparent medium and an opaque dull medium in different directions.
About Diffuse Reflection
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface that has many tiny bumps and dips.
- Diffuse Reflection is how we see all objects.
- Diffuse Reflection does not produce an image.
- Diffuse Reflection still follows the Law of Reflection even though it appears not to because the surface is not perfectly flat. This means parallel incident rays reach the surface at different angles due to all the bumps and dips. Each individual ray follows the Law of Reflection but parallel incident rays do not leave in the same direction as each other.
| Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. Parallel incoming rays are reflected in different directions. This known as scattering. |
References
AQA
- Diffuse reflection, page 203, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Diffuse reflection, page 208, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Diffuse reflection, page 236, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Diffuse reflection, pages 75, 77, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA