Eyes
Key Stage 1
Meaning
Eyes are the part of the body that allows us to see.
About Eyes
- Most animals have only two eyes but some have more and some have no eyes at all.
- Eyes allow us to see colour.
- Eyelids blink a couple of times every minute to keep our eyes moist.
- Eyelashes are there to stop dust getting in our eyes.
- A person whose eyes don't see is called 'blind'.
- Your eyes can be damaged and make you blind if you stare at The Sun.
Examples
| A cat eye. | The eye of a goat. |
| A chamelion's eye. | A crocodile eye. |
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Eyes are the part of the body that allows us to see.
About Eyes
- Most animals have only two eyes but some have more and some have no eyes at all.
- Eyes allow us to see colour.
- Eyelids blink a couple of times every minute to keep our eyes moist.
- Eyelashes are there to stop dust getting in our eyes.
- A person whose eyes don't see is called 'blind'.
- Your eyes can be damaged and make you blind if you stare at The Sun.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The eyes are a pair of sensory organs which allow us to see.
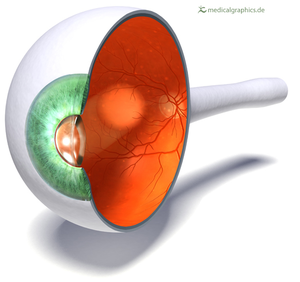
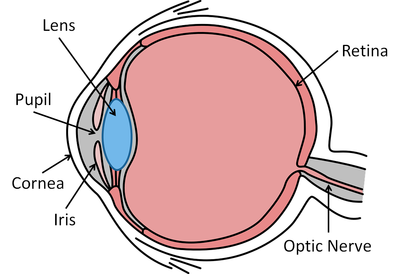
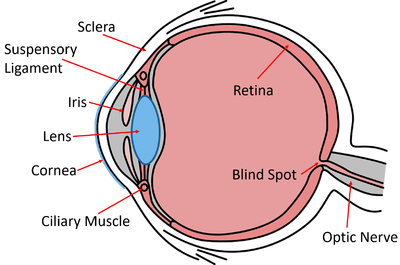
About Human Eyes
- The eye is made of several parts:
- Retina - Detects light.
- Optic Nerve - Sends electrical signals from the eye to the brain.
- Lens - Focuses the light onto the retina.
- Iris - The coloured part of the eye.
- Pupil - The hole in the iris that allows light into the eye.
- Cornea - The outer protective layer of the eye.
| A diagram of the eye. |
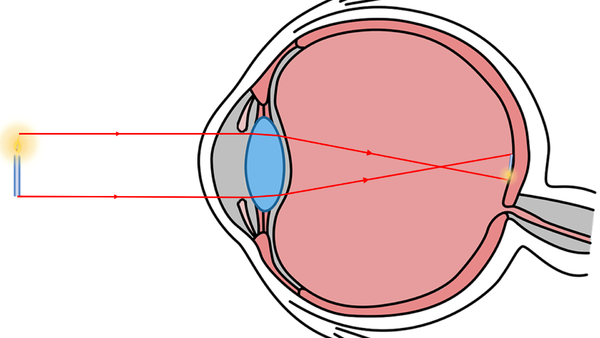
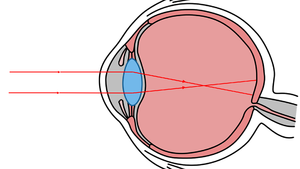
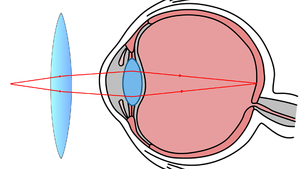
Focusing Images
- The eye uses a lens to focus an image on the retina.
- When the lens does not work well enough people can use glasses.
| The lens refracts the rays of light to form an image of the object. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The eyes are a pair of sensory organs containing receptor cells which can detect light.
About Human Eyes
- The eye is made of several parts:
- Retina - Detects light.
- Optic Nerve - Sends electrical signals from the eye to the brain.
- Lens - Focuses the light onto the retina.
- Iris - The coloured part of the eye.
- Pupil - The hole in the iris that allows light into the eye.
- Cornea - The outer protective layer of the eye.
- Sclera - A protective layer around the eye (the white area around the eye).
- Blind Spot - A point on the back of the eye without any receptor cells to detect light.
- Suspensory Ligaments - Tissue which connects the lens to the ciliary muscles.
- Ciliary Muscles - Muscles which can contract to squeeze the lens and relax to allow the lens to flatten. This is how the lens in the eye focusses light at different distances.
| A diagram of the eye. |
Defects of the Eye
- The eye uses a lens to focus an image on the retina.
- When the lens does not work well enough people require corrective lenses.
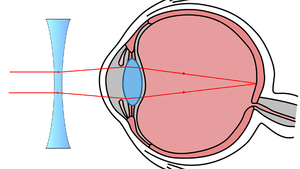
| The lens in the eye of a person with myopia focusses the light from distant objects in front of the retina creating a blurred image. | A myopic person can place a concave lens in front of the eye to correct their vision. |
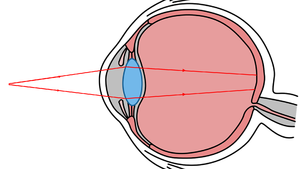
| The lens in the eye of a person with hyperopia focusses the light in behind the retina creating a blurred image. | A hyperopic person can place a convex lens in front of the eye to correct their vision. |
References
AQA
- Eye, page 182, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Eye, pages 140-2, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Eye; defects, page 186, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Eyes, pages 1, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Eyes, pages 154-157, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Eyes, pages 195, 196, 198, 199, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Eyes, pages 70, 71, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Eye, pages 44-45, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Eyes, page 30, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Eyes, pages 78-80, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Eye, pages 90, 92-93, 156, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Eyes, page 44, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR