Nuclear Power
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Nuclear Power is a method used to generate electricity using nuclear fuel.
About Nuclear Power
- Nuclear Fuel can be used to provide power by generating electricity that can be sent to houses and industry.
- Nuclear Fuel has energy in its nuclear potential energy store which can be easily transferred into its thermal energy store.
| A diagram of a coal power station. |
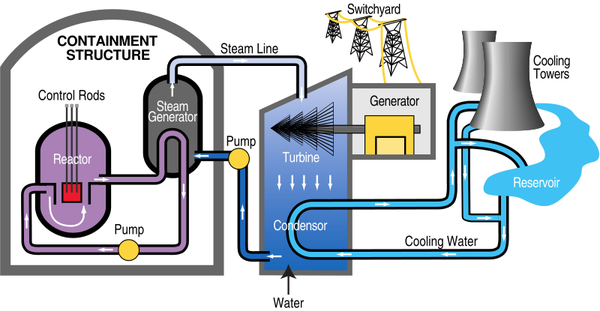
- 1. Nuclear Fuel undergoes a nuclear reaction in the reactor core.
- 2. Water in the reactor core is heated and passed through a heat exchanger.
- 3. Water in the reactor core becomes contaminated with radioactive material so the heat exchanger heats up uncontaminated water.
- 3. The uncontaminated water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can work continuously.
- Power supply can be varied depending on demand.
- Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses.
- High energy density (1kg of Uranium can provide the same energy as 10,000kg of coal).
Disadvantages
- Cost of fuel.
- Difficult to safely dispose of nuclear waste.
- There is a small risk of meltdown.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Nuclear Power is a method used to generate electricity using nuclear fuel.
About Nuclear Power
- Nuclear Fuel can be used to provide power by generating electricity that can be sent to houses and industry.
- Nuclear Fuel has energy in its nuclear potential energy store which can be easily transferred into its thermal energy store.
| A diagram of a coal power station. |
- 1. Nuclear Fuel undergoes a nuclear reaction in the reactor core.
- 2. Water in the reactor core is heated and passed through a heat exchanger.
- 3. Water in the reactor core becomes contaminated with radioactive material so the heat exchanger heats up uncontaminated water.
- 3. The uncontaminated water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can work continuously.
- Power supply can be varied depending on demand.
- Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses.
- High energy density (1kg of Uranium can provide the same energy as 10,000kg of coal).
Disadvantages
- Cost of fuel.
- Difficult to safely dispose of nuclear waste.
- There is a small risk of meltdown.
Extra Information
References
AQA
- Nuclear power, page 121, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Nuclear power, page 178, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Nuclear power, page 278, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Nuclear power, pages 21, 22, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Nuclear power, pages 23, 107, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Nuclear power, pages 37, 42-43, 104-109, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Nuclear power, pages 55, 56, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Nuclear power, pages 57, 58, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA