Plant
Contents
Key Stage 1
Meaning

A plant with the roots showing.
A plant is a living thing that has roots and can make its own food.
About Plants
- Plants usually have a part of them that is green. Most often this is their leaves, but some plants have no leaves like a cactus.
- Some plants are wild and other plants are cultivated.
- We get fruits and vegetables from some plants but some plants have poisonous fruit that we can't eat.
Survival
- To survive a plant needs water, warmth and light.
- An adult plant will wilt if it does not get enough water and then it could die.
- An adult plant will die if it gets too cold and wilt and then die it if gets too hot.
- An adult plant will not be able to make its own food if there is not enough light so the plant will lose its leaves and go into a dormant state.
Germination
- When a seed is planted, if the conditions are right it will germinate and start to grow into an adult plant.
- If there is not enough water, and it is too cold or too hot, the seed will not germinate.
Examples
| A tree is a large plant with a woody trunk. | A flower only grows on flowering plants. |
| A fern is a plant that doesn't grow flowers. | Moss is a small soft plant that can't grow flowers. |
Note for Teachers
- Be careful not to suggest that plants get their food from the soil. Plants only get water and minerals from the soil. The majority of a plant is made using the Carbon Dioxide that the plant absorbed from the air.
- Mushrooms are often mistaken for vegetables which also leads children to falsely identify them as a plant. They are in fact a fungus.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A plant is an organism that makes its own food.
About Plants
- Plants usually have a part of them that is green. Most often this is their leaves, but some plants have no leaves like a cactus.
- Some plants are wild and other plants are cultivated.
- We get fruits and vegetables from some plants but some plants have poisonous fruit that we can't eat.
Survival
- To survive a plant needs water, warmth and light.
- An adult plant will wilt if it does not get enough water and then it could die.
- An adult plant will die if it gets too cold and wilt and then die it if gets too hot.
- An adult plant will not be able to make its own food if there is not enough light so the plant will lose its leaves and go into a dormant state.
Germination
- When a seed is planted, if the conditions are right it will germinate and start to grow into an adult plant.
- If there is not enough water, and it is too cold or too hot, the seed will not germinate.
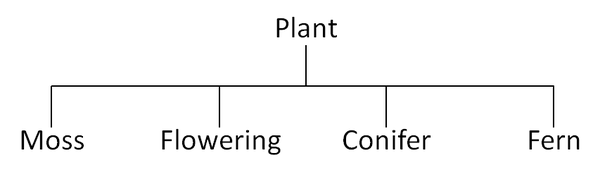
Classification of Plants
| Moss | Flowering Plants | Conifer | Fern |
References
AQA
- Plant; cells, page 11, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Plant; diseases, page 55, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Plant; growth, pages 81, 82, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Plant; hormones, pages 81, 82, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Plants, pages 236-237, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants, pages 36, 67-77, 124-5, 202, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; adaptations, pages 268, 272-273, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; cells, pages 5-7, 23, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; cloning, pages 29, 31, 179, 226, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; competition, pages 236-7, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; Competition, pages 75-6, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; defence systems, page 106, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; defences, pages 94-95, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; diseases, pages 102-9, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; diseases, pages 87, 92-95, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; Effects of abiotic factors, pages 78-9, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; genetic engineering, pages 224-225, 230-231, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; hormones, pages 169-76, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; hormones, pages 176-179, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; organ systems, pages 71-2, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; organs, pages 62-63, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; organs, pages 70-1, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; reproduction, pages 200-201, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; selective breeding, pages 222-223, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; tissues, page 68-70, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Plants; transpiration, pages 66-69, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Plants; transport, pages 12-13, 18-21, 23, 62-65, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
Edexcel
- Plant; cells, page 12, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; cells, page 24, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; defences against disease, page 160, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; defences against disease, page 57, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; diseases (detection of), page 161, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; extracts, page 181, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; extracts, page 64, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; hormones, pages 215-219, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Plant; hormones, pages 74, 75, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Plants, pages 102, 196-199, 213, 253, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; active transport, page 63, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; asexual reproduction, pages 152-153, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; cell walls, page 219, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; cells, pages 19, 25, 60, 218-219, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; cuticles, pages 218-219, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; defences of, pages 218-219, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; glucose production, pages 47, 50, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; gravitropism, pages 110-111, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; hormones, pages 110-113, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; identification keys, page 181, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Nutrient cycling, pages 140-141, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Pathogens, page 210, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Photosynthesis, pages 46-53, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Phototropism, pages 110-111, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Populations, pages 284-285, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Sampling, pages 182-183, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Selective breeding, pages 198-199 Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; Starch tests, pages 48-49, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; stem cells, page 69, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; transpiration, pages 80-83, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; transport system, pages 73, 78-79, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; tropism, pages 110-111, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; water loss, pages 80-83, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Plants; wilting, page 81, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR