Key Stage 2
Meaning

A
mirror reflects light so we can see a perfect image.
Reflection from shiny surfaces is when light bounces off a material creating an image that we can see.
- Singular Noun: Reflection
- Plural Noun: Reflections
- Verb: To reflect
- Adjective: Reflective
About Reflection form Shiny Surfaces
- When a surface is shiny we can see a reflection on the surface.
- A mirror is a shiny piece of metal that reflects all of the light that hits it and allows us to see an image.
- Mirrors are said to be reflective.
- If a surface is dull you cannot see an image and it is not called reflective, but it still reflects the light.
|
|
|
| You can see the reflection of the mountain and clouds on the surface of the water.
|
The glass reflects the image of the clouds.
|
|
|
|
| These glasses are very reflective.
|
You can sometimes see a reflection is a person's eye.
|
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Specular Reflection is when light bounces off a flat surface to produce a an image.
About Specular Reflection
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
|
|
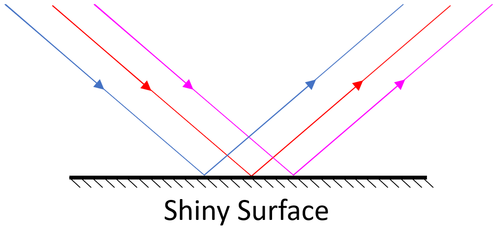
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. Parallel rays are reflected and stay parallel to one another.
|
The Law of Reflection
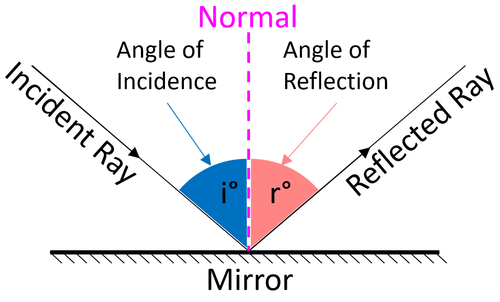
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Specular Reflection is when an Electromagnetic Wave bounces off the interface between a transparent medium and an opaque medium with a flat surface to produce an image.
About Specular Reflection
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
|
|
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. Parallel rays are reflected and stay parallel to one another.
|
The Law of Reflection
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
References
AQA
- Specular reflection, page 203, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Specular reflection, page 208, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Specular reflection, page 235, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Specular reflection, pages 75, 77, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Specular reflection, page 115, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Specular reflection, page 38, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Specular reflection, page 68, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
OCR
- Specular reflection, pages 165, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR