Wind Power
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Wind Power is an energy resource that uses the flow of the wind to generate electricity.
About Wind Power
- Wind Power is a renewable energy resource.
- Wind has energy in the kinetic energy store of the moving air.
Power
Wind Power can be used to generate electricity.
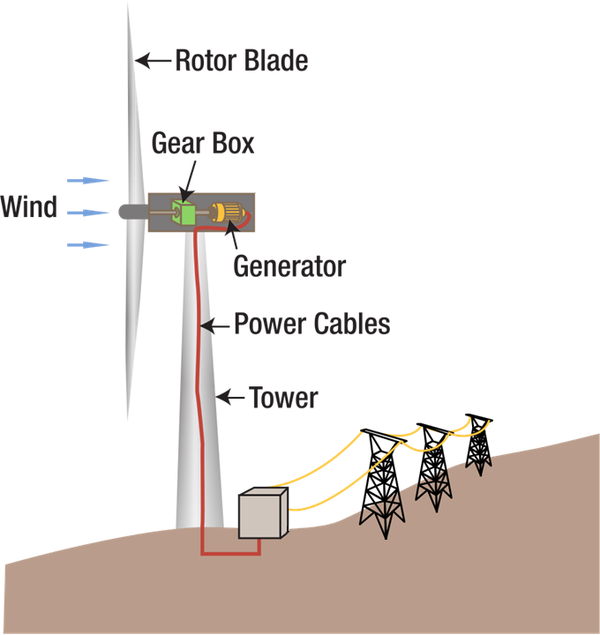
| A diagram of a Wind Turbine. |
- 1. Wind moves past the rotary blades of the turbine.
- 2. The turbine spins.
- 3. The turbine causes the generator to turn.
- 4. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can provide power in places not connected to the national grid.
- Do not produce pollution.
- The running cost is almost nothing.
- No fuel cost.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Need over a thousand to generate the power that a single coal power station would make.
- Only work when it’s windy (70-80% of the time)
- If it is too windy they have to be stopped for safety.
- They produce a lot of noise, annoying local people.
- Cannot increase power output when more is needed.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Wind Power is an energy resource that uses the flow of the wind to generate electricity.
About Wind Power
- Wind Power is a renewable energy resource.
- Wind has energy in the kinetic energy store of the moving air.
Power
Wind Power can be used to generate electricity.
| A diagram of a Wind Turbine. |
- 1. Wind moves past the rotary blades of the turbine.
- 2. The turbine spins.
- 3. The turbine causes the generator to turn.
- 4. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can provide power in places not connected to the national grid.
- Do not produce pollution.
- The running cost is almost nothing.
- No fuel cost.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Need over a thousand to generate the power that a single coal power station would make.
- Only work when it’s windy (70-80% of the time)
- If it is too windy they have to be stopped for safety.
- They produce a lot of noise, annoying local people.
- Cannot increase power output when more is needed.
References
AQA
- Wind power, page 176, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Wind power, page 19, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Wind power, page 228, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Wind power, page 24, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Wind power, page 279, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Wind power, page 38, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Wind power, page 47, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Wind power, page 49, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Wind power, pages 32-3, 41, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Wind power, page 161, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Wind power, page 29, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel