Difference between revisions of "Background Radiation"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== '''Background radiation''' is the natural ionising radiation all around from different sources in the environment. ==...") |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
====Sources of Background Radiation==== | ====Sources of Background Radiation==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:BackgroundRadiation.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''Food''': | ||
| + | Many of our foods contain small quantities of radioactive isotopes. Figure A shows a Banana containing Potassium-40, a gamma emitter. The Potassium-40 in your body means the average person emits around 108 gamma rays every second. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The Ground''': Rocks under the ground have small quantities of radioactive isotopes and so gamma rays are being emitted from beneath our feet all the time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Radon Gas''': Rocks containing Uranium decay by alpha emission to Radium and then Radium decays into Radon. This gas escapes through cracks in the ground and we breath in the radioactive radon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Cosmic Ray]]s''': The explosions of stars throughout space sends out extremely fast moving particles. Many of these arrive at earth. When they do they are usually stopped by atoms in the atmosphere. However some few will make it to the ground, so we are constantly bombarded by tiny pieces of debris from exploding stars. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Medical Uses''': Modern medicine uses a number of techniques which rely on radioactive isotopes or other sources of ionising radiation. There is a limited number of X-rays, CAT scans and PET scans you are allowed to have in a year in order to stop you receiving a dangerous dose. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 23:06, 9 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Background radiation is the natural ionising radiation all around from different sources in the environment.
About Background Radiation
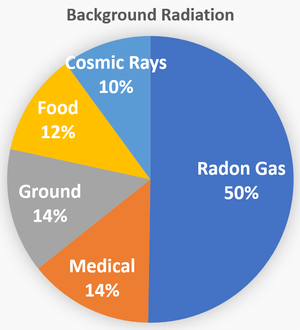
- There are several sources of background radiation including food, rocks in the ground, Radon gas and cosmic rays.
- The level of background radiation a person is exposed to depends on their diet, job and where they spend their time.
- Pilots are exposed to a higher than average level of background radiation because at high altitude people are exposed to more cosmic rays.
- Miners are exposed to a higher than average level of background radiation because many rocks are sources of ionising radiation.
- Hospital workers are exposed to a higher than average level of background radiation because sources of ionising radiation are used in medical imaging.
Sources of Background Radiation
| Food:
Many of our foods contain small quantities of radioactive isotopes. Figure A shows a Banana containing Potassium-40, a gamma emitter. The Potassium-40 in your body means the average person emits around 108 gamma rays every second. The Ground: Rocks under the ground have small quantities of radioactive isotopes and so gamma rays are being emitted from beneath our feet all the time. Radon Gas: Rocks containing Uranium decay by alpha emission to Radium and then Radium decays into Radon. This gas escapes through cracks in the ground and we breath in the radioactive radon. Cosmic Rays: The explosions of stars throughout space sends out extremely fast moving particles. Many of these arrive at earth. When they do they are usually stopped by atoms in the atmosphere. However some few will make it to the ground, so we are constantly bombarded by tiny pieces of debris from exploding stars. Medical Uses: Modern medicine uses a number of techniques which rely on radioactive isotopes or other sources of ionising radiation. There is a limited number of X-rays, CAT scans and PET scans you are allowed to have in a year in order to stop you receiving a dangerous dose. |