Difference between revisions of "Crude Oil"
(→Power) |
(→Key Stage 4) |
||
| Line 90: | Line 90: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:85px; text-align:center;" |70+ | | style="height:20px; width:85px; text-align:center;" |70+ | ||
| style="height:20px; width:85px; text-align:center;" |Not distilled. | | style="height:20px; width:85px; text-align:center;" |Not distilled. | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:350px; text-align:center;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:350px; text-align:center;" |Tar for roads. |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 3 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Crude Oil is a Fossil Fuel formed from the remains of dead sea creatures trapped in the sediment at the bottom of the sea.
About Crude Oil
- Crude Oil is a non-renewable energy resource.
- Crude Oil has energy in its chemical potential energy store which can be transferred into a thermal energy store by combustion.
Power
- Crude Oil can be used to provide power directly buy burning it in homes, cars, trains. planes and in furnaces or it can provide power by generating electricity.
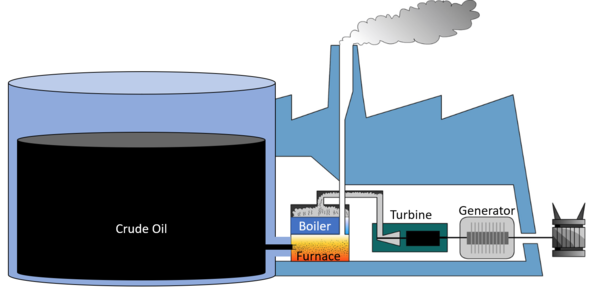
| A diagram of an oil power station. |
- 1. Crude Oil is burned in a furnace.
- 2. Water is heated in a boiler by the burning oil.
- 3. Water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can work continuously.
- Power supply can be varied depending on demand.
- Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses.
Disadvantages
- Cost of fuel.
- Produce Carbon Dioxide contributing to global warming.
- Other pollutants produced which can harm health or produce acid rain.
- Crude Oil will run out.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Crude oil is a mixture of different hydrocarbons, mostly alkanes, formed in an anoxic environment over millions of years from the remains of dead sea creatures trapped in the sediment at the bottom of the sea.
About Crude Oil
- Crude oil is known as a Fossil Fuel.
- Crude oil is a non-renewable energy resource so once it is used it cannot be replaced within our lifetime.
- Modern technology relies heavily on crude oil as both a fuel and a feedstock for producing plastics.
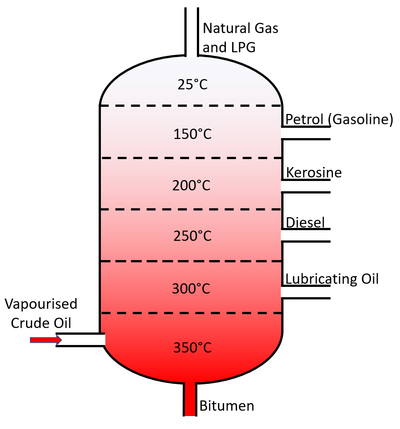
Crude oil can be separated by fractional distillation into different 'fractions' which have different applications:
| Fraction | Carbon Chain Length | Boiling Point (°C) | Application |
| Natural Gas | 1-2 | -160 to -89 | Fuel for heating homes and gas power stations. |
| LPG | 3-4 | -42 to -1 | Fuel for heating homes and gas power stations. |
| Petrol (Gasoline) | 5-10 | 20 to 200 | Fuel for cars and feedstock for plastic manufacture. |
| Kerosine | 10-16 | 180 to 260 | Fuel for Planes. |
| Diesel | 14-20 | 260 to 340 | Fuel for cars, trucks and trains. |
| Lubricating Oil | 20-50 | 370 to 600 | Lubrication for machines. |
| Bitumen | 70+ | Not distilled. | Tar for roads. |
| A diagram showing a fractional distillation tower. |
| Fraction | Natural Gas | LPG | Petrol | Kerosene | Diesel | Lubricating Oil | Bitumen |
| Carbon Chain Length | 1-2 | 3-4 | 5-10 | 10-16 | 14-20 | 20-50 | 70+ |
| Boiling Point | |||||||
| Viscosity | |||||||
| Flammability | |||||||
| Volatility | |||||||