Difference between revisions of "Supernova"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: When a [[massive]] [[star]] runs out of [[Helium]] to [[Nuclear Fusion|fuse]] the core collapses rapidly. Eventually the [[element]]s collide with one another and rebound outwards into an explosion known as a [[supernova]] which can be brighter than all the other [[star]]s in a [[galaxy]] put together. | : When a [[massive]] [[star]] runs out of [[Helium]] to [[Nuclear Fusion|fuse]] the core collapses rapidly. Eventually the [[element]]s collide with one another and rebound outwards into an explosion known as a [[supernova]] which can be brighter than all the other [[star]]s in a [[galaxy]] put together. | ||
: The [[supernova]] will leave behind a core which is either a [[Neutron Star|neutron star]] or a [[Black Hole|black hole]] depending on its [[mass]]. The greater [[mass]] becomes a [[Black Hole|black hole]]. | : The [[supernova]] will leave behind a core which is either a [[Neutron Star|neutron star]] or a [[Black Hole|black hole]] depending on its [[mass]]. The greater [[mass]] becomes a [[Black Hole|black hole]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Beyond the Curriculum== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jf_4z4AKwJg}} | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 20 April 2019
Key Stage 4
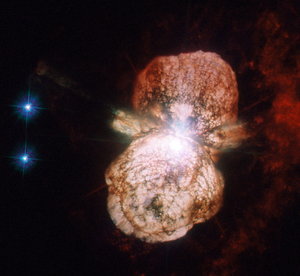
An artist's impression of a supernova.
Meaning
A supernova is the explosion of a red super giant which happens when it has run out of Helium to fuse.
About Supernovae
- When a massive star runs out of Helium to fuse the core collapses rapidly. Eventually the elements collide with one another and rebound outwards into an explosion known as a supernova which can be brighter than all the other stars in a galaxy put together.
- The supernova will leave behind a core which is either a neutron star or a black hole depending on its mass. The greater mass becomes a black hole.