Difference between revisions of "Electrostatic Force"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==Key Stage | + | ==Key Stage 4== |
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
The '''electrostatic force''' is a [[force]] that causes [[Electrical Charge|charged]] [[object]]s to be [[attract|attracted]] or [[repel|repelled]] by one another. | The '''electrostatic force''' is a [[force]] that causes [[Electrical Charge|charged]] [[object]]s to be [[attract|attracted]] or [[repel|repelled]] by one another. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
: The '''electrostatic force''' is what holds [[ion]]s together in an [[Ionic Bond|ionic bond]]. | : The '''electrostatic force''' is what holds [[ion]]s together in an [[Ionic Bond|ionic bond]]. | ||
: [[Proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] experience the '''electrostatic force''' of repulsion and in order for [[Nuclear Fusion|fusion]] to occur [[proton]]s must have enough [[energy]] to overcome this [[force]] of repulsion. | : [[Proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] experience the '''electrostatic force''' of repulsion and in order for [[Nuclear Fusion|fusion]] to occur [[proton]]s must have enough [[energy]] to overcome this [[force]] of repulsion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Electrostatic forces, page 119, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Electrostatic forces, pages 209, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Electrostatic forces, page 178, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Electrostatic forces, page 34, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Electrostatic forces, pages 23, 59, 60, 66, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Electrostatics, pages 94-95, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:14, 5 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The electrostatic force is a force that causes charged objects to be attracted or repelled by one another.
About The Electrostatic Force
- Electrostatic Force is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- Electrostatic Force is a non-contact force because it can act without objects touching.
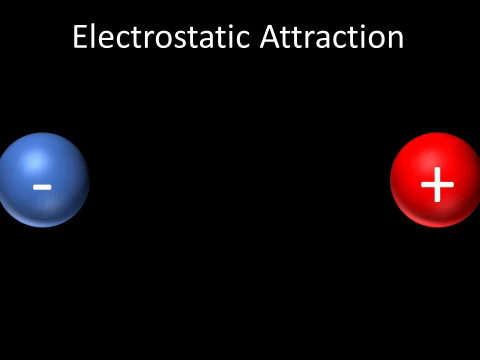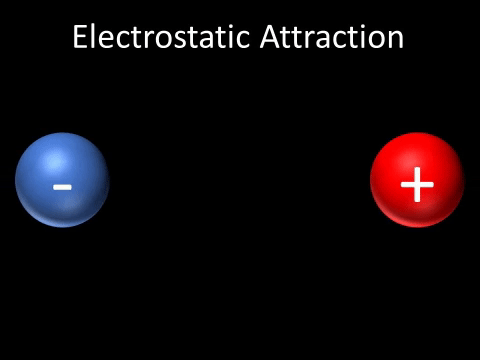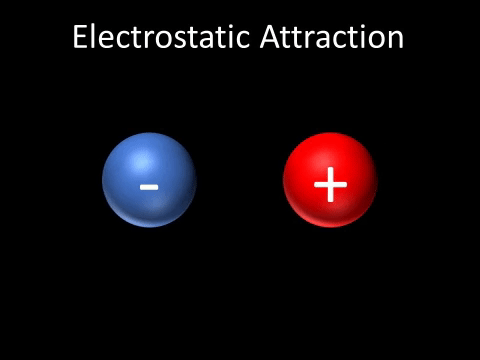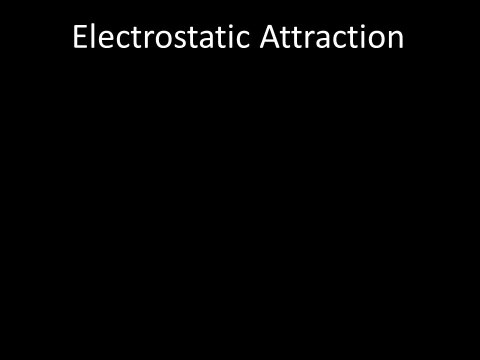
| A positively charged and negatively charged object will be attracted to each other. |
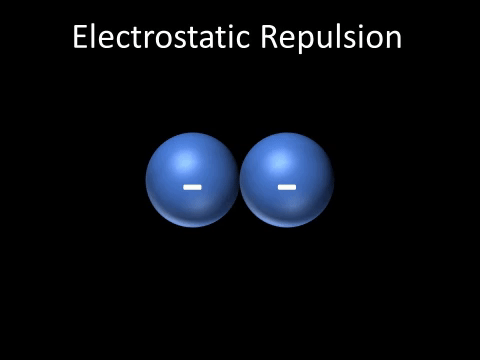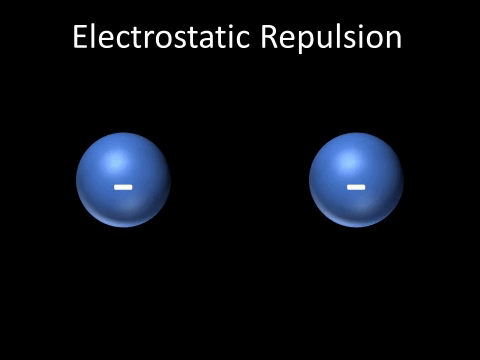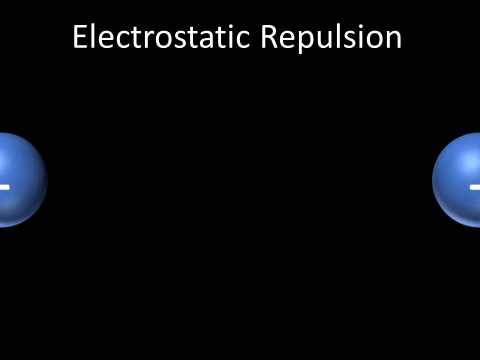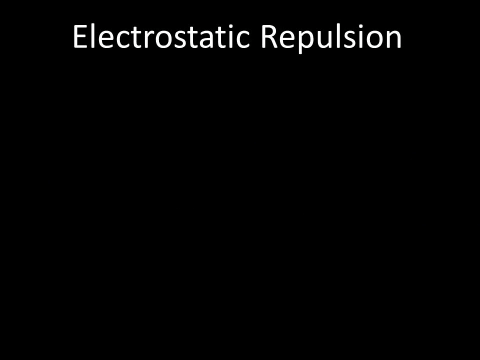
| Two negatively charged objects repel each other. |
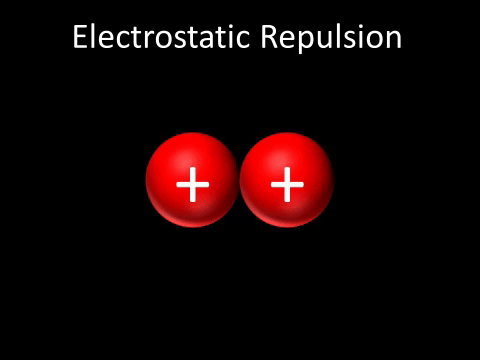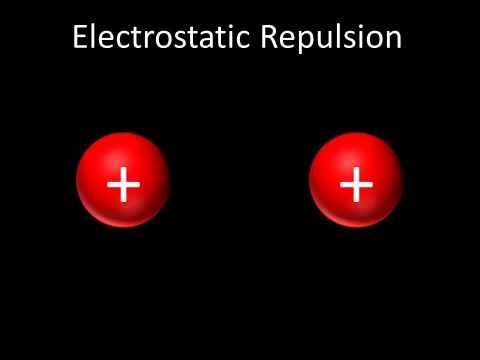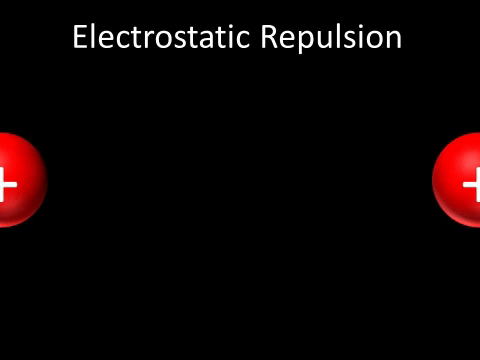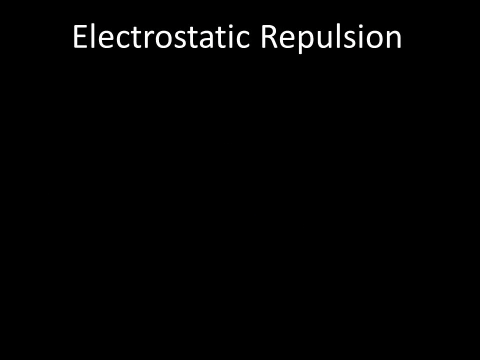
| Two positively charged objects repel each other. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The electrostatic force is a force that causes charged objects to be attracted or repelled by one another.
About The Electrostatic Force
- Electrostatic Force is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- Electrostatic Force is a non-contact force because it can act without objects touching.
- A positively charged and negatively charged object will be attracted to each other.
- Two negatively charged objects repel each other.
- Two positively charged objects repel each other.
- The electrostatic force is what holds ions together in an ionic bond.
- Protons in the nucleus experience the electrostatic force of repulsion and in order for fusion to occur protons must have enough energy to overcome this force of repulsion.
References
AQA
- Electrostatic forces, page 119, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Electrostatic forces, pages 209, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Electrostatic forces, page 178, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Electrostatic forces, page 34, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel