Difference between revisions of "Thinking Distance"
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Thinking distances, pages 22, 23, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Thinking distances, pages 22, 23, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Thinking distances, pages 49, 51, 52, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Thinking distances, pages 49, 51, 52, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Thinking distance, pages 218-221, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Thinking distances, page 210, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:48, 20 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
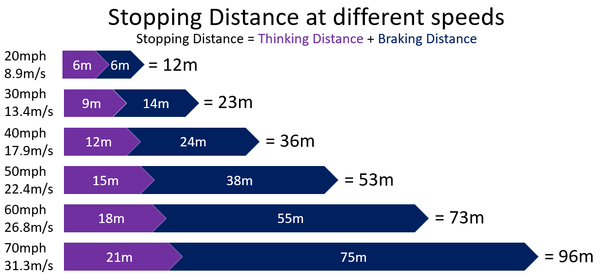
Thinking distance is the distance a car travels between the moment a hazard appears and the moment the driver responds to it by applying the brakes.
About Thinking Distance
Thinking distance depends on:
- The speed of the vehicle - The greater the speed the larger the thinking distance.
- The reaction time of the driver - The longer the reaction time the longer the thinking distance and therefore stopping distance.
- Thinking distance can be affected by drugs such as stimulants and depressants. Stimulants allow you to react faster so there is a shorter reaction time and therefore a shorter thinking distance. Depressants slow reactions so there is a longer reaction time and therefore a longer thinking distance.
- Alcohol is a depressant so it increases thinking distance making it dangerous to drive after drinking alcohol.
- Tiredness increases reaction time which increases thinking distance which makes driving while tired more dangerous.
References
AQA
- Thinking distance, braking, pages 242, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Thinking distance, page 164, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Thinking distance, page 166, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Thinking distance, page 215, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thinking distance, pages 148-149, 157, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Thinking distance, pages 67, 69, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thinking distances, pages 176-178, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Thinking distances, pages 208-210, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Thinking distance, page 26, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Thinking distances, page 155, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Thinking distances, pages 22, 23, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Thinking distances, pages 49, 51, 52, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel