Difference between revisions of "Neuron"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[neuron]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[neuron]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Neurons=== | ||
| + | : [[Neuron]]s join together to form [[nerve]]s. | ||
| + | : The point where two [[neuron]]s meet is called a [[synapse]]. | ||
| + | : At the [[synapse]] between two [[neuron]]s the [[Impulse (Biology)|electrical impulse]] must be [[transmit]]ed across the gap. | ||
Revision as of 10:36, 12 November 2018
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A nerve cell is a specialised cell in animals which transmits electrical impulses around the body.
Adaptations of Nerve Cells
- Nerve Cells have an elongated shape to send electrical impulses more quickly.
- Nerve Cells have branches called dendrites to link up to other nerve cells.
About Nerve Cells
- All nerves in the body are made of nerve cells.
- Nerve cells are specially adapted to send electrical signals quickly.
- Many nerve cells grouped together make nerve tissue.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Neurons are specialised cells in the nervous system which transmits electrical impulses around the body.
Adaptations of Neurons
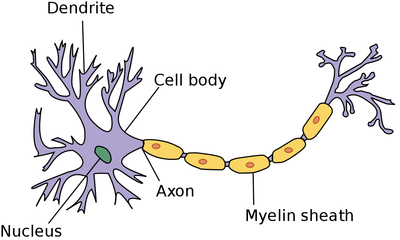
- Neurons have an elongated axon to send electrical impulses more quickly.
- Neurons have branches called dendrites to link up to other neurons.
- The axon of a neuron is covered in a myelin sheath which acts as an electrical insulator to maintain the strength of the impulse as it passes along the axon.
| A diagram of a neuron. |
About Neurons
- Neurons join together to form nerves.
- The point where two neurons meet is called a synapse.
- At the synapse between two neurons the electrical impulse must be transmited across the gap.