Difference between revisions of "Anomaly"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AnomalousResult1.png|center|225px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:AnomalousResult2.png|center|375px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
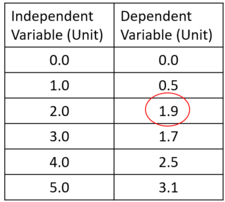
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The '''anomalous''' result, circled in red, can be spotted because it doesn't fit the pattern of increasing by around 0.6 each time. | ||
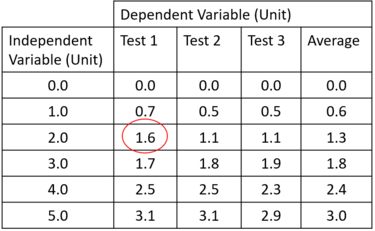
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The '''anomalous''' result, circled in red, can be spotted because it is higher than all the other results in the row. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 30 November 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An anomaly is an unusual result that does not fit the pattern formed by the rest of the results.
About Anomalies
- Anomalies may be caused by experimental errors such as an uncontrolled variable.
- An anomaly can be spotted by looking for a pattern in the results and any results that don't fit that pattern.
- An anomaly may become clear from a graph of results where it is easier to see the pattern.
Examples
| The anomalous result, circled in red, can be spotted because it doesn't fit the pattern of increasing by around 0.6 each time. | The anomalous result, circled in red, can be spotted because it is higher than all the other results in the row. |