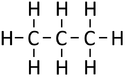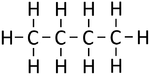Difference between revisions of "Alkane"
(→Reactions of Alkanes) |
|||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
=====Incomplete Combustion===== | =====Incomplete Combustion===== | ||
| + | [[Incomplete Combustion|Incomplete combustion]] occurs when there is not enough [[Oxygen]] to [[Oxidise]] all of the [[atom]]s in the [[alkane]]. | ||
| + | During [[Incomplete Combustion|incomplete combustion]] of [[alkane]]s the [[product]]s may include [[Carbon]] ([[soot]]) and [[Carbon Monoxide]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : Methane + Oxygen → Carbon + Water | ||
| + | : <chem>CH4 + O2 -> C + 2H2O</chem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : Methane + Oxygen → Carbon Monoxide + Water | ||
| + | : <chem>CH4 + 1.5O2 -> CO + 2H2O</chem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : Ethane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water | ||
| + | : <chem>2C2H6 + 7O2 -> 4CO2 + 6H2O</chem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : Propane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water | ||
| + | : <chem>C3H8 + 5O2 -> 3CO2 + 4H2O</chem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : Butane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water | ||
| + | : <chem>2C4H10 + 13O2 -> 8CO2 + 10H2O</chem> | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 17 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Alkanes are the simplest form of hydrocarbon compounds with no double bonds and the general formula; CnH2n+2
About Alkanes
- Alkanes are a homologous series of hydrocarbon compounds.
- The functional group of the Alkanes is the single bonds between the Carbon atoms and between the Carbon and Hydrogen atoms.
- Alkanes are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with single bonds and Hydrogen atoms taking the remaining bonds.
Examples
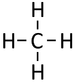
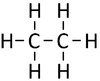
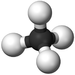
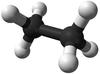
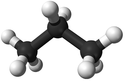
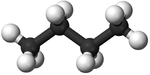
| Methane | Ethane | Propane | Butane | |
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | CH4 | C2H6 | C3H8 | C4H10 |
| Structural Formula | CH4 | CH3CH3 | CH3CH2CH3 | CH3CH2CH2CH3 |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |
Reactions of Alkanes
Combustion
During combustion of alkanes the Carbon and Hydrogen atoms are oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
Complete Combustion
Complete combustion occurs when there is enough Oxygen to completely Oxidise all of the atoms in the alkane. In the complete combustion of alkanes the only products are Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Methane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>CH4 + 2O2 -> CO2 + 2H2O</chem>
- Ethane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C2H6 + 7O2 -> 4CO2 + 6H2O</chem>
- Propane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>C3H8 + 5O2 -> 3CO2 + 4H2O</chem>
- Butane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C4H10 + 13O2 -> 8CO2 + 10H2O</chem>
Incomplete Combustion
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough Oxygen to Oxidise all of the atoms in the alkane. During incomplete combustion of alkanes the products may include Carbon (soot) and Carbon Monoxide.
- Methane + Oxygen → Carbon + Water
- <chem>CH4 + O2 -> C + 2H2O</chem>
- Methane + Oxygen → Carbon Monoxide + Water
- <chem>CH4 + 1.5O2 -> CO + 2H2O</chem>
- Ethane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C2H6 + 7O2 -> 4CO2 + 6H2O</chem>
- Propane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>C3H8 + 5O2 -> 3CO2 + 4H2O</chem>
- Butane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C4H10 + 13O2 -> 8CO2 + 10H2O</chem>