Difference between revisions of "Thinking Distance"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
*The [[speed]] of the vehicle - The greater the [[speed]] the larger the '''thinking distance'''. | *The [[speed]] of the vehicle - The greater the [[speed]] the larger the '''thinking distance'''. | ||
*The [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] of the driver - The longer the [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] the longer the [[Thinking Distance|thinking distance]] and therefore '''stopping distance'''. | *The [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] of the driver - The longer the [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] the longer the [[Thinking Distance|thinking distance]] and therefore '''stopping distance'''. | ||
| − | : '''Thinking distance''' can be affected by drugs such as [[stimulant]]s and [[depressant]]s. [[Stimulant]]s allow you to react faster so there is a shorter [[Reaction Time|reaction time]] and therefore a shorter '''thinking distance'''. [[Depressant]]s slow reactions so there is a longer [[Reaction Time|reaction time]] and therefore a longer '''thinking distance'''. | + | : '''Thinking distance''' can be affected by drugs such as [[stimulant]]s and [[depressant]]s. [[Stimulant]]s allow you to react faster so there is a shorter [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] and therefore a shorter '''thinking distance'''. [[Depressant]]s slow reactions so there is a longer [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] and therefore a longer '''thinking distance'''. |
: [[Alcohol (Drug)|Alcohol]] is a [[depressant]] so it increases '''thinking distance''' making it dangerous to drive after drinking [[Alcohol (Drug)|alcohol]]. | : [[Alcohol (Drug)|Alcohol]] is a [[depressant]] so it increases '''thinking distance''' making it dangerous to drive after drinking [[Alcohol (Drug)|alcohol]]. | ||
| + | : Tiredness increases [[Human Reaction Time|reaction time]] which increases '''thinking distance''' which makes driving while tired more dangerous. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 11:03, 17 February 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
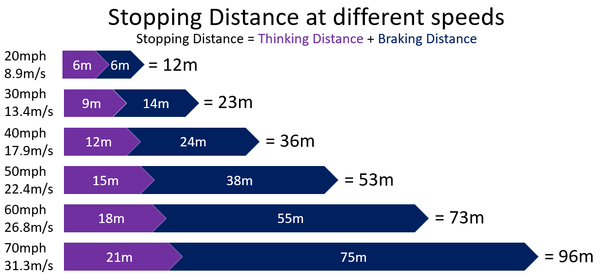
Thinking distance is the distance a car travels between the moment a hazard appears and the moment the driver responds to it by applying the brakes.
About Stopping Distance
Thinking distance depends on:
- The speed of the vehicle - The greater the speed the larger the thinking distance.
- The reaction time of the driver - The longer the reaction time the longer the thinking distance and therefore stopping distance.
- Thinking distance can be affected by drugs such as stimulants and depressants. Stimulants allow you to react faster so there is a shorter reaction time and therefore a shorter thinking distance. Depressants slow reactions so there is a longer reaction time and therefore a longer thinking distance.
- Alcohol is a depressant so it increases thinking distance making it dangerous to drive after drinking alcohol.
- Tiredness increases reaction time which increases thinking distance which makes driving while tired more dangerous.