Difference between revisions of "Hydroelectric"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== '''Hydroelectricity''' is an energy resource that uses the water flowing in rivers to generate electricity. ===About Hydroel...") |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Power=== | ===Power=== | ||
| − | '''Hydroelectricity''' can be used to generate electricity | + | '''Hydroelectricity''' can be used to generate [[electricity]]. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:HydroelectricDamDiagram.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:HydroelectricDamDiagram.png|center|600px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[ | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[hydroelectric]] dam. |
|} | |} | ||
: 1. Water flowing down a river is held back by a dam making a large reservoir. | : 1. Water flowing down a river is held back by a dam making a large reservoir. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
: 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin. | : 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin. | ||
: 5. The generator makes an electrical current. | : 5. The generator makes an electrical current. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Advantages==== | ||
| + | *Reliable source as it is built in places that do not suffer drought. | ||
| + | *Power provided can change at a moments notice by allowing more water through the turbines. | ||
| + | *Low running costs and no fuel cost. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Disadvantages==== | ||
| + | *Expensive to build. | ||
| + | *Require the flooding of a large area of land. | ||
| + | *Destroys habitat of some creatures. | ||
| + | *Blocks the migration of some river species. | ||
| + | *Can only be built in certain locations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qef-f2KobIY}} | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Hydroelectricity''' is an [[Energy Resource|energy resource]] that uses the water flowing in rivers to generate electricity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Hydroelectricity=== | ||
| + | : '''Hydroelectricity''' is a [[Renewable Energy Resource|renewable energy resource]]. | ||
| + | : '''Hydroelectricity''' has [[energy]] in the [[Gravitational Potential Energy Store|gravitational potential energy store]] of water that is flowing downhill. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Power=== | ||
| + | '''Hydroelectricity''' can be used to generate [[electricity]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:HydroelectricDamDiagram.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[hydroelectric]] dam. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | : 1. Water flowing down a river is held back by a dam making a large reservoir. | ||
| + | : 2. Some water is allowed through pipes to flow downhill. | ||
| + | : 3. This water turns a turbine as it falls. | ||
| + | : 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin. | ||
| + | : 5. The generator makes an electrical current. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Advantages==== | ||
| + | *Reliable source as it is built in places that do not suffer drought. | ||
| + | *Power provided can change at a moments notice by allowing more water through the turbines. | ||
| + | *Low running costs and no fuel cost. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Disadvantages==== | ||
| + | *Expensive to build. | ||
| + | *Require the flooding of a large area of land. | ||
| + | *Destroys habitat of some creatures. | ||
| + | *Blocks the migration of some river species. | ||
| + | *Can only be built in certain locations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Hydroelectic power, page 50, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09992 ''Hydroelectric power, page 177, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Hydroelectric power, page 24, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Hydroelectric power, page 279, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Hydroelectric power, page 52, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac242 ''Hydroelectric power, pages 18, 20, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Hydroelectric power, pages 32-3, 41, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Hydroelectric power, pages 38-39, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Hydro-electricity, page 161, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Hydro-electricity, page 29, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Hydroelectricity, page 326, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Hydroelectricity, page 44, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Hydroelectric power, pages 229, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:59, 12 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Hydroelectricity is an energy resource that uses the water flowing in rivers to generate electricity.
About Hydroelectricity
- Hydroelectricity is a renewable energy resource.
- Hydroelectricity has energy in the gravitational potential energy store of water that is flowing downhill.
Power
Hydroelectricity can be used to generate electricity.
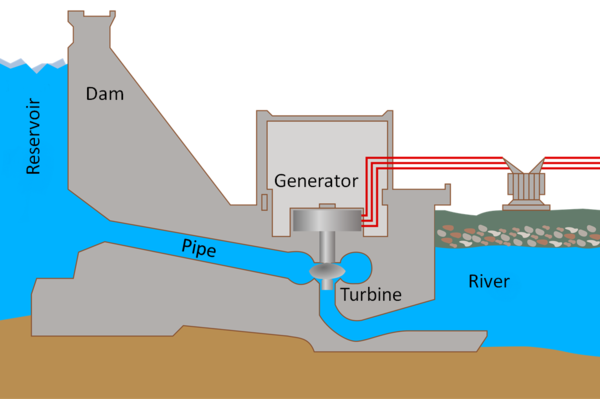
| A diagram of a hydroelectric dam. |
- 1. Water flowing down a river is held back by a dam making a large reservoir.
- 2. Some water is allowed through pipes to flow downhill.
- 3. This water turns a turbine as it falls.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Reliable source as it is built in places that do not suffer drought.
- Power provided can change at a moments notice by allowing more water through the turbines.
- Low running costs and no fuel cost.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Require the flooding of a large area of land.
- Destroys habitat of some creatures.
- Blocks the migration of some river species.
- Can only be built in certain locations.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Hydroelectricity is an energy resource that uses the water flowing in rivers to generate electricity.
About Hydroelectricity
- Hydroelectricity is a renewable energy resource.
- Hydroelectricity has energy in the gravitational potential energy store of water that is flowing downhill.
Power
Hydroelectricity can be used to generate electricity.
| A diagram of a hydroelectric dam. |
- 1. Water flowing down a river is held back by a dam making a large reservoir.
- 2. Some water is allowed through pipes to flow downhill.
- 3. This water turns a turbine as it falls.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Reliable source as it is built in places that do not suffer drought.
- Power provided can change at a moments notice by allowing more water through the turbines.
- Low running costs and no fuel cost.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Require the flooding of a large area of land.
- Destroys habitat of some creatures.
- Blocks the migration of some river species.
- Can only be built in certain locations.
References
AQA
- Hydroelectic power, page 50, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, page 177, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, page 24, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, page 279, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, page 52, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, pages 18, 20, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, pages 32-3, 41, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Hydroelectric power, pages 38-39, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
Edexcel
- Hydro-electricity, page 161, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Hydro-electricity, page 29, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Hydroelectricity, page 326, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Hydroelectricity, page 44, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel