Difference between revisions of "Culturing Micro-organisms"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
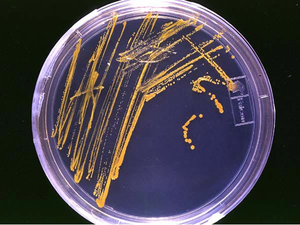
| − | [[File:CulturingBacteria.png|right|300px|thumb|This picture shows [[micro- | + | [[File:CulturingBacteria.png|right|300px|thumb|This picture shows [[micro-organism]]s being '''cultured''' on a [[Culture Medium|culture medium]].]] |
'''Culturing Micro-organisms''' is growing [[micro-organism]]s under controlled conditions to produce large numbers of them. | '''Culturing Micro-organisms''' is growing [[micro-organism]]s under controlled conditions to produce large numbers of them. | ||
===About Culturing Micro-organisms=== | ===About Culturing Micro-organisms=== | ||
| − | : '''Culturing Micro-organisms''' is used to identify types of [[micro-organism]] when the initial sample has too few [[micro- | + | : '''Culturing Micro-organisms''' is used to identify types of [[micro-organism]] when the initial sample has too few [[micro-organism]]s to test. |
| − | : [[Micro- | + | : [[Micro-organism]]s are '''cultured''' on a [[Culture Medium|culture medium]] which is a source of [[nutrient]]s and [[water]] that the [[micro-organism]]s need to [[growth|grow]] and [[reproduction|reproduce]]. |
| − | : When '''culturing micro-organisms''' the most important part is not allowing your [[Culture Medium|culture medium]] to be contaminated by other [[micro- | + | : When '''culturing micro-organisms''' the most important part is not allowing your [[Culture Medium|culture medium]] to be contaminated by other [[micro-organism]]s. To ensure this [[scientist]]s follow an [[Aseptic Technique|aseptic technique]]. |
===Method=== | ===Method=== | ||
| + | : 1. Heat an [[Inoculating Loop|inoculating loop]] over a [[Bunsen Burner|bunsen]] flame until it is red hot. This sterilises the [[Inoculating Loop|inoculating loop]]. (Do not place the [[Inoculating Loop|inoculating loop]] down or breath on it as this may contaminate it.) | ||
| + | : 2. Dip the [[Inoculating Loop|inoculating loop]] into a sample of [[micro-organism]]s. | ||
| + | : 3. Slide the lid of the [[Petri Dish|petri dish]] just enough to create space for the [[Inoculating Loop|inoculating loop]] then wipe the [[Inoculating Loop|inoculating loop]] across the top of the [[Culture Medium|culture medium]]. Then replace the lid as quickly as possible. This helps reduce the chance of contamination. | ||
| + | : 4. Tape the sides of the [[Petri Dish|petri dish]] lid down to prevent contamination of the [[Culture Medium|culture medium]], but leave it loose enough that [[air]] can get in to ensure the [[micro-organism]]s get enough [[Oxygen]]. Otherwise only [[anaerobic]] [[micro-organism]]s will grow. | ||
| + | : 5. Label the [[Petri Dish|petri dish]] clearly and incubate at 25°C. Do not incubate at higher [[temperature]]s as this may lead to [[pathogen]]ic [[micro-organism]]s being '''cultured'''. | ||
Latest revision as of 12:51, 8 April 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Culturing Micro-organisms is growing micro-organisms under controlled conditions to produce large numbers of them.
About Culturing Micro-organisms
- Culturing Micro-organisms is used to identify types of micro-organism when the initial sample has too few micro-organisms to test.
- Micro-organisms are cultured on a culture medium which is a source of nutrients and water that the micro-organisms need to grow and reproduce.
- When culturing micro-organisms the most important part is not allowing your culture medium to be contaminated by other micro-organisms. To ensure this scientists follow an aseptic technique.
Method
- 1. Heat an inoculating loop over a bunsen flame until it is red hot. This sterilises the inoculating loop. (Do not place the inoculating loop down or breath on it as this may contaminate it.)
- 2. Dip the inoculating loop into a sample of micro-organisms.
- 3. Slide the lid of the petri dish just enough to create space for the inoculating loop then wipe the inoculating loop across the top of the culture medium. Then replace the lid as quickly as possible. This helps reduce the chance of contamination.
- 4. Tape the sides of the petri dish lid down to prevent contamination of the culture medium, but leave it loose enough that air can get in to ensure the micro-organisms get enough Oxygen. Otherwise only anaerobic micro-organisms will grow.
- 5. Label the petri dish clearly and incubate at 25°C. Do not incubate at higher temperatures as this may lead to pathogenic micro-organisms being cultured.