Difference between revisions of "Neuron"
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|[[File:NeuronDiagram.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:NeuronDiagram.png|center|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[neuron]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[Motor Neuron|motor '''neuron''']]. |
|} | |} | ||
===About Neurons=== | ===About Neurons=== | ||
| − | : | + | : '''Neurons''' join together to form [[nerve]]s. |
| − | : The point where two | + | : The point where two '''neurons''' meet is called a [[synapse]]. |
| − | : At the [[synapse]] between two | + | : At the [[synapse]] between two '''neurons''' the [[Impulse (Biology)|electrical impulse]] must be [[transmit]]ed across the gap. |
| + | There are three different types of '''neuron''' you should know: | ||
| + | *[[Sensory Neuron]] | ||
| + | *[[Relay Neuron]] | ||
| + | *[[Motor Neuron]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Nerve cells, page 14, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10095 ''Nerve cells, page 14, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Nerve cells, page 31, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Nerve cells, page 31, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Nerve cells, page 9, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851338/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851338&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=425855d5890466e47189e1c21b67a1ea ''Nerve cells, pages 8, 9, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:09, 9 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A nerve cell is a specialised cell in animals which transmits electrical impulses around the body.
Adaptations of Nerve Cells
- Nerve Cells have an elongated shape to send electrical impulses more quickly.
- Nerve Cells have branches called dendrites to link up to other nerve cells.
About Nerve Cells
- All nerves in the body are made of nerve cells.
- Nerve cells are specially adapted to send electrical signals quickly.
- Many nerve cells grouped together make nerve tissue.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Neurons are specialised cells in the nervous system which transmits electrical impulses around the body.
Adaptations of Neurons
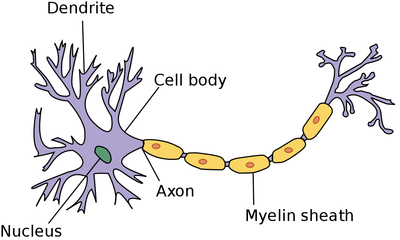
- Neurons have an elongated axon to send electrical impulses more quickly.
- Neurons have branches called dendrites to link up to other neurons.
- The axon of a neuron is covered in a myelin sheath which acts as an electrical insulator to maintain the strength of the impulse as it passes along the axon.
| A diagram of a motor neuron. |
About Neurons
- Neurons join together to form nerves.
- The point where two neurons meet is called a synapse.
- At the synapse between two neurons the electrical impulse must be transmited across the gap.
There are three different types of neuron you should know:
References
AQA
- Nerve cells, page 14, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Nerve cells, page 14, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Nerve cells, page 31, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Nerve cells, page 31, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Nerve cells, page 9, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Nerve cells, pages 8, 9, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA