Difference between revisions of "GCSE Physics Required Practical: Investigating Mechanical Waves"
(→Method) |
(→Improving Precision) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
====Improving [[Accuracy]]==== | ====Improving [[Accuracy]]==== | ||
: Count the number of [[wave]]s over a greater period of [[time]] greater than 10 [[second]]s to reduce the effect of [[Human Error|human error]] on the [[frequency]]. | : Count the number of [[wave]]s over a greater period of [[time]] greater than 10 [[second]]s to reduce the effect of [[Human Error|human error]] on the [[frequency]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Experiment 2: Waves on a String=== | ===Experiment 2: Waves on a String=== | ||
Revision as of 09:31, 25 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Investigate the features of mechanical waves.
Experiment 1: Ripple Tank
Method
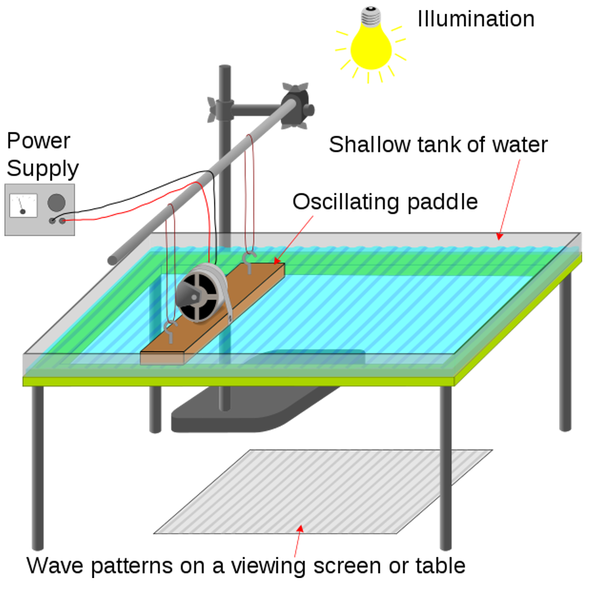
| A diagram of the apparatus used to investigate the features of mechanical waves. |
- Set up the equipment as shown in the diagram.
- Count the number of waves that pass a given point over 10 seconds.
- Divide the number of waves by the 10 seconds to find the frequency of the waves.
- Measure the length of the ripple tank from paddle to end using a ruler.
- Use a stopwatch to time how long it takes for a wave to travel this displacement.
- Use the equation \(v=\frac{s}{t}\) to find the velocity of the wave.
- Use the equation \(v=f \lambda\) to find the wavelength of the wave.
Improving Accuracy
- Count the number of waves over a greater period of time greater than 10 seconds to reduce the effect of human error on the frequency.
Experiment 2: Waves on a String
Method
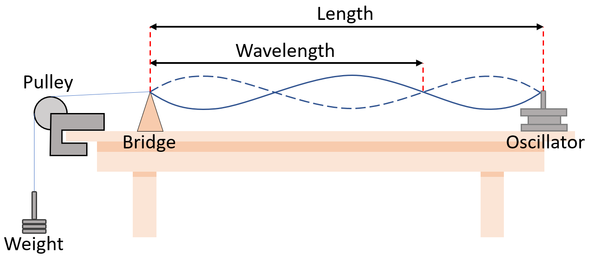
| A diagram of the apparatus used to investigate the features of a wave on a string. |
- Set up the equipment as shown in the diagram.
- Adjust the frequency of the oscillator until it produces a clear wave on the string.
- Record the frequency of the oscillator.
- Measure the wavelength of the wave using a ruler.
- Use the equation \(v=f \lambda\) to find the wavespeed of the wave.
- Repeat for different 5 frequencies of the wave.
Improving Precision
- Calculate an average for the wave speed over a greater number of results to reduce the effect of random errors, improving the precision.