Difference between revisions of "Mean Average"
(→Key Stage 4) |
|||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
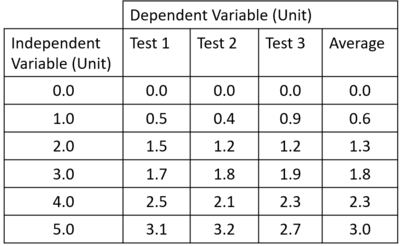
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Mean Average|average]] for each set of [[results]] can be calculated by adding a row together and dividing by the number of [[results]] in that row. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Mean Average|average]] for each set of [[results]] can be calculated by adding a row together and dividing by the number of [[results]] in that row. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Averages (means), page 14, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Averages (means), page 14, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d50 ''Averages (means), page 7, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Averages, page 13, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Averages, page 14, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac27 ''Averages, page 6, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Averages, pages 260, 262, 281, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Averages, pages 262-263, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 28 October 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A mean average is when you add up a set of numbers and divide by how many of numbers were added.
About a Mean Average
- A mean average is used in science to reduce the effects of random errors in the results of an experiment.
Calculating a Mean Average
Results: 5,3
\(Average = \tfrac{5+3}{2}\)
\(Average = 4\)
Results: 7.0, 6.8, 7.8
\(Average = \tfrac{7.0+6.8+7.8}{3}\)
\(Average = 7.1\)
Results: 12.3, 11.7, 11.4, 12.1
\(Average = \tfrac{12.3+11.7+11.4+12.1}{4}\)
\(Average = 11.875\) In science the answer should be rounded to the same number of significant figures as the original numbers.
\(Average = 11.9\)
Examples
| The average for each set of results can be calculated by adding a row together and dividing by the number of results in that row. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A mean average is when you add up a set of numbers and divide by how many of numbers were added.
About a Mean Average
- A mean average is used in science to reduce the effects of random errors in the results of an experiment.
Calculating a Mean Average
Results: 5,3
\(Average = \tfrac{5+3}{2}\)
\(Average = 4\)
Results: 7.0, 6.8, 7.8
\(Average = \tfrac{7.0+6.8+7.8}{3}\)
\(Average = 7.1\)
Results: 12.3, 11.7, 11.4, 12.1
\(Average = \tfrac{12.3+11.7+11.4+12.1}{4}\)
\(Average = 11.875\) In science the answer should be rounded to the same number of significant figures as the original numbers.
\(Average = 11.9\)
Examples
| The average for each set of results can be calculated by adding a row together and dividing by the number of results in that row. |
References
AQA
- Averages (means), page 14, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Averages (means), page 14, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Averages (means), page 7, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Averages, page 13, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Averages, page 14, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Averages, page 6, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Averages, pages 260, 262, 281, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Averages, pages 262-263, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA