Difference between revisions of "Membrane Bound Organelle"
(→Examples) |
(→Examples) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
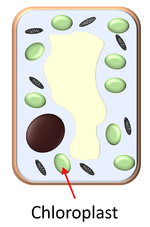
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The [[chloroplast]] is a '''membrane bound [[organelle]]''' found in [[Plant Cell|plant cells]] and some [[protist]]s. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The [[chloroplast]] is a '''membrane bound [[organelle]]''' found in [[Plant Cell|plant cells]] and some [[protist]]s. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:Mitochondrion.png|center|300px]] |
|[[File:PermanentVacuole.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:PermanentVacuole.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 09:27, 23 June 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A membrane bound organelle is a structure inside a cell that performs a particular function (an organelle) which is covered in a surface membrane.
About Membrane Bound Organelles
- The membrane surrounding a membrane bound organelle is selectively permeable membrane allowing the organelle to select which chemicals can enter and leave through the membrane.
Examples
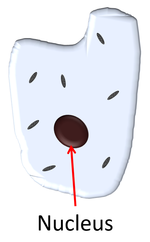
| The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle in all eukaryotic cells. | The chloroplast is a membrane bound organelle found in plant cells and some protists. |
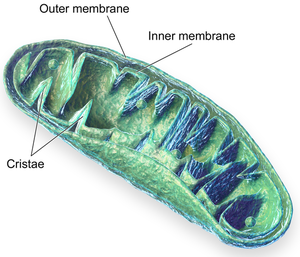
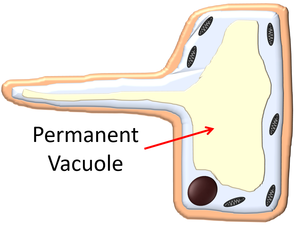
| A mitochondrion is a membrane bound organelle found in in all eukaryotic cells. | The permanent vacuole is a membrane bound organelle found in plant cells. |