Difference between revisions of "Active Site"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Active sites, page 143, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Active sites, page 143, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Active sites, page 36, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Active sites, page 36, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Active site (enzymes), pages 32-33, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Active sites, page 15, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Active sites, page 17, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:13, 30 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
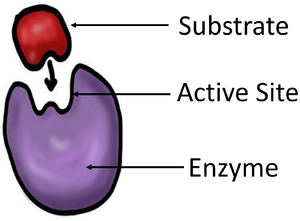
Meaning
An active site is the part of an enzymes which is where the enzyme interacts with a substrate.
About the Active Site
- The active site is shaped to fit with only one substrate so enzymes all have specific roles in an organism.
- When an enzyme becomes denatured the substrate can no longer fit into the active site preventing the enzyme from functioning.
References
AQA
- Active sites, page 109, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Active sites, page 115, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Active sites, page 25, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Active sites, page 28, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Active sites, page 42, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Active sites, page 49, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Active site of an enzyme, page 18, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Active site of an enzyme, pages 14, 257, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Active sites, page 143, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Active sites, page 36, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel