Difference between revisions of "Graphene"
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Graphene, page 24, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Graphene, page 24, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Graphene, page 63, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Graphene, page 63, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Graphene, page 21, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Graphene, page 94, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:21, 11 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
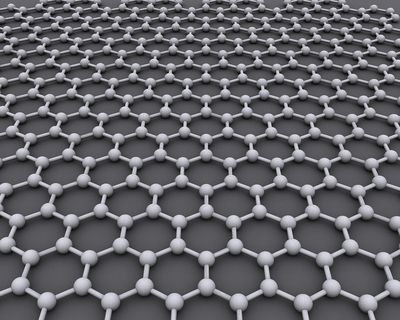
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon in which the atoms are bonded in a hexagonal arrangement in a single layer.
| A diagram showing the arrangement of carbon atoms in graphene. |
About Graphene
- Graphene is a giant covalent structure.
- Graphene is a single layer of graphite.
- Graphene is a good electrical conductor because it only uses 3 out of the 4 electrons in the outer shell to bond with other atoms allowing the last electron to move freely around the giant covalent structure.
- Large sheets of graphene are extremely strong which is a very useful property. A layer of graphene as thin as cling film could support the weight of an entire elephant.
References
AQA
- Graphene, page 88, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Graphene, page 90, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Graphene, page 119, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Graphene, page 34, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Graphene, page 51, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Graphene, page 55, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Graphene, pages 167-8, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Graphene, pages 84-5, 88, 343, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Grapheme, page 44, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Graphene, page 188, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Graphene, page 24, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Graphene, page 63, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel