Difference between revisions of "Diffraction"
(→Depictions of Diffraction) |
|||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:SingleSlitDiffraction.png|center|200px]] | + | |[[File:SingleSlitDiffraction.png|center|200px|link=https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/wave-interference/latest/wave-interference_all.html]] |
| − | |[[File:DoubleSlitDiffraction.png|center|200px]] | + | |[[File:DoubleSlitDiffraction.png|center|200px|link=https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/wave-interference/latest/wave-interference_all.html]] |
|- | |- | ||
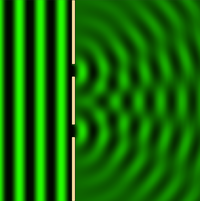
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This image shows a plan view of '''diffraction''' of a [[wave]] through a [[Single Slit Diffraction|single slit]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This image shows a plan view of '''diffraction''' of a [[wave]] through a [[Single Slit Diffraction|single slit]]. To explore this yourself using physics simulations, visit the website 'phet' by clicking on the image. |
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This image shows a plan view of '''diffraction''' of a [[wave]] through a [[Double Slit Diffraction|double slit]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This image shows a plan view of '''diffraction''' of a [[wave]] through a [[Double Slit Diffraction|double slit]]. To explore this yourself using physics simulations, visit the website 'phet' by clicking on the image. |
| + | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 16:52, 23 May 2024
Key Stage 5
Meaning
Diffraction is the spreading of waves when they pass through a gap or around an obstacle.
About Diffraction
- Diffraction occurs with all types of waves, including light, sound, and water waves.
- Diffraction is evidence for the wave-like behaviour of matter.
- The extent of diffraction depends on the wavelength of the wave and the size of the gap or obstacle.
- Diffraction is most noticeable when the gap size is comparable to the wavelength.
- Diffraction explains phenomena such as the bending of light around corners and the formation of diffraction patterns.
- Diffraction is used in various applications, including X-ray diffraction to determine crystal structures and electron diffraction to study the properties of materials.
Depictions of Diffraction
| This image shows a plan view of diffraction of a wave through a single slit. To explore this yourself using physics simulations, visit the website 'phet' by clicking on the image. | This image shows a plan view of diffraction of a wave through a double slit. To explore this yourself using physics simulations, visit the website 'phet' by clicking on the image. |
Examples
- Diffraction patterns are observed when light passes through a single slit.
- Diffraction of sound waves allows us to hear around corners.