Difference between revisions of "Gestation"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
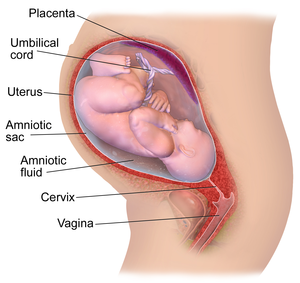
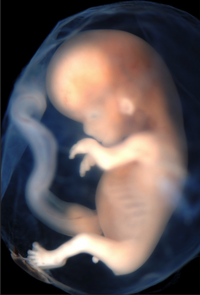
| + | [[File:PregnancyDiagram.png|right|300px|thumb|A [[diagram]] showing the final stage of gestation just before the [[offspring]] is born.]] | ||
[[Gestation]] is the period of time while [[offspring]] is developing in the [[uterus]] of a [[mammal]]. | [[Gestation]] is the period of time while [[offspring]] is developing in the [[uterus]] of a [[mammal]]. | ||
===About Gestation=== | ===About Gestation=== | ||
: [[Gestation]] starts with [[conception]] and ends with [[birth]] of the [[offspring]]. | : [[Gestation]] starts with [[conception]] and ends with [[birth]] of the [[offspring]]. | ||
| − | + | The [[offspring]] goes through several stages of development: | |
| + | : 1. The [[ovum]] is released from the [[ovary]]. | ||
| + | : 2. The [[ovum]] is [[fertilised]] by a [[Sperm Cell|sperm]]. | ||
| + | : 3. The [[embryo]] makes its way to the [[uterus]] where it implants itself into the lining of the [[uterus]]. | ||
| + | : 4. The lining of the [[uterus]] develops into an [[Amnion|amniotic sac]], a [[placenta]] and an [[Umbilical Cord|umbilical]] cord to protect and feed the [[embryo]]. | ||
| + | : 5. The [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] specialise and the [[embryo]] becomes a [[foetus]]. | ||
| + | : 6. The [[foetus]] becomes fully developed and turns itself upside down so it can exit through the [[vagina]] head first. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 07:43, 20 September 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gestation is the period of time while offspring is developing in the uterus of a mammal.
About Gestation
- Gestation starts with conception and ends with birth of the offspring.
The offspring goes through several stages of development:
- 1. The ovum is released from the ovary.
- 2. The ovum is fertilised by a sperm.
- 3. The embryo makes its way to the uterus where it implants itself into the lining of the uterus.
- 4. The lining of the uterus develops into an amniotic sac, a placenta and an umbilical cord to protect and feed the embryo.
- 5. The cells specialise and the embryo becomes a foetus.
- 6. The foetus becomes fully developed and turns itself upside down so it can exit through the vagina head first.
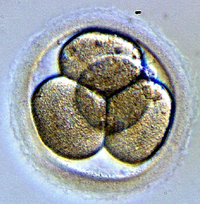
| After fertilisation the ovum divides into two cells, then four cells. | This embryo has many cells that have not yet been given a specific job. |
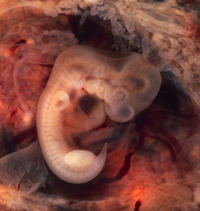
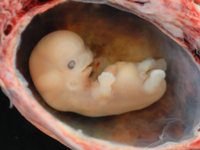
| The cells in this embryo are being assigned specific jobs as it starts to look more like a human. | Once all the cells have been given their specific jobs it is called a foetus. A this point the offspring is preparing to live outside the uterus. |