Difference between revisions of "Wave Power"
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
: 3. The air turns a turbine. | : 3. The air turns a turbine. | ||
: 4. The turbine turns a generator. | : 4. The turbine turns a generator. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Advantages==== | ||
| + | *Do not produce pollution. | ||
| + | *No fuel costs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Disadvantages==== | ||
| + | *Expensive to build. | ||
| + | *Require many of them to generate meaningful amounts of power. | ||
| + | *Can only be built on the coast. | ||
| + | *Hazardous to boats. | ||
| + | *Unreliable because they are dependent on wind. | ||
| + | *Damages the habitats of sea creatures. | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 9 October 2018
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Wave Power is an energy resource that uses the movement of waves on the water to generate electricity.
About Wave Power
- Wave Power is a renewable energy resource.
- Wave Power has energy in the kinetic energy store of water waves.
Power
Wave Power can be used to generate electricity.
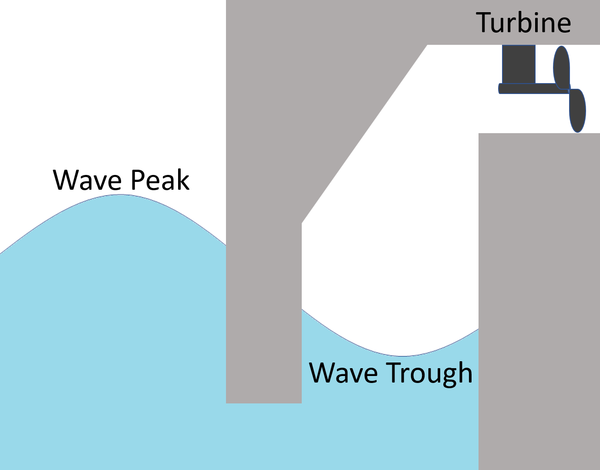
| A diagram of a wave generator. |
- 1. Water rises and falls inside a chamber due to the waves.
- 2. The water forces air to rush in and out of a chamber through pipes.
- 3. The air turns a turbine.
- 4. The turbine turns a generator.
Advantages
- Do not produce pollution.
- No fuel costs.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Require many of them to generate meaningful amounts of power.
- Can only be built on the coast.
- Hazardous to boats.
- Unreliable because they are dependent on wind.
- Damages the habitats of sea creatures.