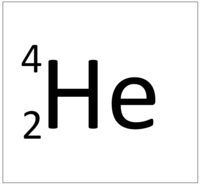Difference between revisions of "Relative Atomic Mass"
m (NRJC moved page Atomic Mass to Relative Atomic Mass) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[File:ElementTile.png|right|400px|thumb|An [[element]] tile showing the '''mass number'''.]] | [[File:ElementTile.png|right|400px|thumb|An [[element]] tile showing the '''mass number'''.]] | ||
| − | The | + | The '''Atomic Mass''' or '''mass number''' is the number of [[nucleon]]s ([[proton]]s + [[neutron]]s) in an [[atom]]. |
===About The Atomic Mass=== | ===About The Atomic Mass=== | ||
Revision as of 12:05, 23 November 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
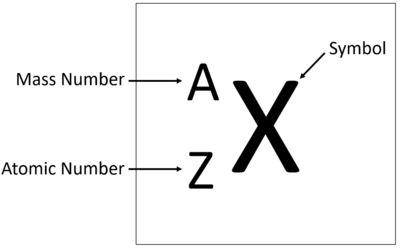
An element tile showing the mass number.
The Atomic Mass or mass number is the number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in an atom.
About The Atomic Mass
- Two atoms of the same element may have the same Atomic Number but a different Atomic Mass depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Elements with different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- The atomic mass is not affected by the number of electrons.
- Only the particles in the nucleus affect the atomic mass.
Examples
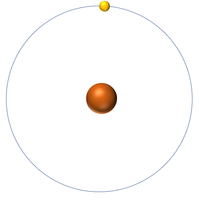
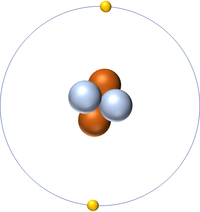
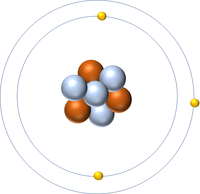
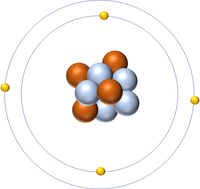
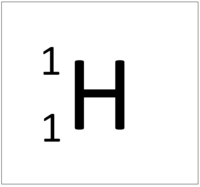
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has one nucleon so it has an atomic mass of 1. | Helium has four nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 4. | Lithium has seven nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 7. | Beryllium has eleven nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 11. |