Difference between revisions of "Crude Oil"
(→Key Stage 4) |
(→Power) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|[[File:CrudeOilPowerStationDiagram2.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:CrudeOilPowerStationDiagram2.png|center|600px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
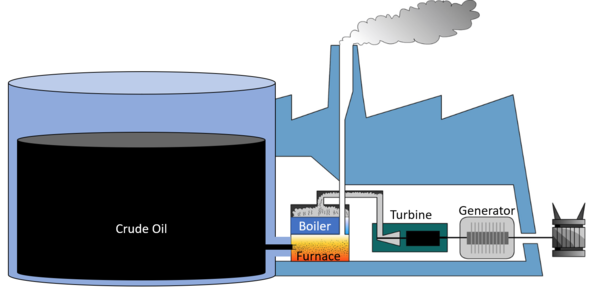
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of an oil [[power station]]. |
|} | |} | ||
: 1. Crude Oil is burned in a furnace. | : 1. Crude Oil is burned in a furnace. | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 15 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Crude Oil is a Fossil Fuel formed from the remains of dead sea creatures trapped in the sediment at the bottom of the sea.
About Crude Oil
- Crude Oil is a non-renewable energy resource.
- Crude Oil has energy in its chemical potential energy store which can be transferred into a thermal energy store by combustion.
Power
- Crude Oil can be used to provide power directly buy burning it in homes, cars, trains. planes and in furnaces or it can provide power by generating electricity.
| A diagram of an oil power station. |
- 1. Crude Oil is burned in a furnace.
- 2. Water is heated in a boiler by the burning oil.
- 3. Water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can work continuously.
- Power supply can be varied depending on demand.
- Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses.
Disadvantages
- Cost of fuel.
- Produce Carbon Dioxide contributing to global warming.
- Other pollutants produced which can harm health or produce acid rain.
- Crude Oil will run out.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Crude oil is a non-renewable energy resource and a feedstock for producing plastics.
About Crude Oil
- Crude oil is a mixture of different hydrocarbons