Difference between revisions of "Sensory Neuron"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Sensory Neurons=== | ===About Sensory Neurons=== | ||
: '''Sensory neurons''' [[transmit]] the [[Impulse (Biology)|electrical impulse]] produced by the [[Receptor Cell|receptor cells]] to the [[Relay Neuron|relay neurons]] in the [[Spinal Cord|spinal cord]]. | : '''Sensory neurons''' [[transmit]] the [[Impulse (Biology)|electrical impulse]] produced by the [[Receptor Cell|receptor cells]] to the [[Relay Neuron|relay neurons]] in the [[Spinal Cord|spinal cord]]. | ||
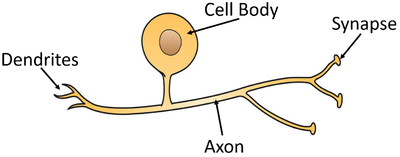
| − | : The [[Receptor Cell|receptor cell]]s sends an [[Impulse (Biology)|electrical impulse]] into the [[dendrite]]s, past the cell body, down the [[axon]] and to the [[synapse]] where the '''sensory neuron''' connects to a [[Relay Neuron| | + | : The [[Receptor Cell|receptor cell]]s sends an [[Impulse (Biology)|electrical impulse]] into the [[dendrite]]s, past the cell body, down the [[axon]] and to the [[synapse]] where the '''sensory neuron''' connects to a [[Relay Neuron|relay neuron]]. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 10:30, 3 June 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A sensory neuron is a specialsed cell in the nervous system which transmits an electrical impulse to the central nervous system.
About Sensory Neurons
- Sensory neurons transmit the electrical impulse produced by the receptor cells to the relay neurons in the spinal cord.
- The receptor cells sends an electrical impulse into the dendrites, past the cell body, down the axon and to the synapse where the sensory neuron connects to a relay neuron.
| A diagram of a sensory neuron. |