Difference between revisions of "Ovary"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f394 ''Ovary, ovaries, pages 191, 208-9, 250, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f394 ''Ovary, ovaries, pages 191, 208-9, 250, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f395 ''Ovary, ovaries; follicle, page 208-9, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f395 ''Ovary, ovaries; follicle, page 208-9, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Ovaries, page 142, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Ovaries, pages 225, 230, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''Ovaries, pages 77, 79, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Revision as of 11:27, 24 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
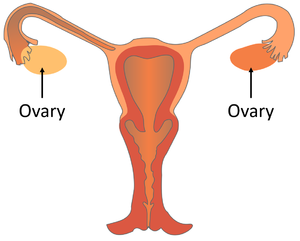
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system which produces and stores the egg cells.
About the Ovary
- There are two ovaries in a female.
- The ovaries release one ovum every 28 days.
- Each ovary takes a turn to release the ovum each month, but in some female humans both ovaries release an ovum at the same time which can lead to twins.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The ovaries are organs in the female reproductive system and endocrine glands in the endocrine system.
About Ovaries in the Female Reproductive System
- The ovaries are where the ova are stored.
- During the menstrual cycle follicle stimulating hormone causes a follicle in the ovary grow and a single ovum to mature.
- Luteinising Hormone causes the ovum to be released from the follicle.
About Ovaries as Endocrine Glands
- Ovaries secrete a hormone called oestrogen.
- Oestrogen causes the expression of female characteristics during puberty including the widening of the hips, breast growth and the initiation of the menstrual cycle.
References
AQA
- Ovaries, page 182, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Ovaries, page 208, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Ovaries, pages 160-161, 168-169, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Ovaries, pages 61, 63, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Ovaries, pages 73, 77, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Ovaries, pages12, 13, 17, 18, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Ovary, ovaries, pages 191, 208-9, 250, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Ovary, ovaries; follicle, page 208-9, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA