Difference between revisions of "Supernova"
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Supernovae, pages 234-235, 241, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Supernovae, pages 234-235, 241, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Supernovae, pages 252, 253, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Supernovae, pages 252, 253, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Supernova, page 123, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Supernovae, page 188, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:50, 29 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
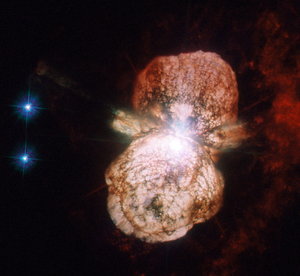
An artist's impression of a supernova.
Meaning
A supernova is the explosion of a red super giant which happens when it has run out of Helium to fuse.
About Supernovae
- When a massive star runs out of Helium to fuse the core collapses rapidly. Eventually the elements collide with one another and rebound outwards into an explosion known as a supernova which can be brighter than all the other stars in a galaxy put together.
- The supernova will leave behind a core which is either a neutron star or a black hole depending on its mass. The greater mass becomes a black hole.
Beyond the Curriculum
References
AQA
- Supernova, pages 285, 287, 291, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Supernovae, page 319, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Supernovae, pages 100, 102, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Supernovae, pages 234-235, 241, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Supernovae, pages 252, 253, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA