Difference between revisions of "Nuclear Fuel"
(→Power) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Nuclear Fuel''' is a [[radioactive]] [[material]] which can be used to generate electricty. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Nuclear Fuel=== | ||
| + | : '''Nuclear Fuel''' has [[energy]] in its [[Nuclear Potential Energy Store|nuclear potential energy store]] which can be easily transferred into its [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy store]]. | ||
| + | : The most common '''nuclear fuels''' are [[Uranium-235]] and [[Plutonium-239]]. | ||
| + | : '''Nuclear Fuel''' transfers energy to the [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy store]] during a [[Nuclear Reaction|nuclear reaction]]. | ||
| + | : '''Nuclear Fuel''' is very dangerous because it is [[radioactive]] which causes harm to living [[organism]]s.: | ||
| + | : When '''nuclear fuel''' is used the waste products are still [[radioactive]] so they must be buried deep underground where they cannot harm living [[organism]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Power=== | ||
| + | : [[Nuclear Fuel]] can be used to provide [[power]] by generating electricity that can be sent to houses and industry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
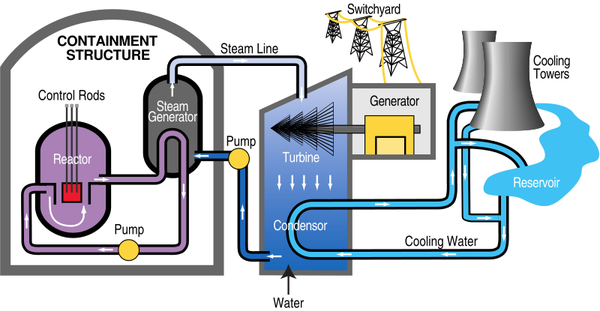
| + | |[[File:NuclearPowerStationDiagram.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[coal]] [[power station]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | : 1. '''Nuclear Fuel''' undergoes a [[Nuclear Reaction|nuclear reaction]] in the [[Reactor Core|reactor core]]. | ||
| + | : 2. Water in the [[Reactor Core|reactor core]] is heated and passed through a [[Heat Exchanger|heat exchanger]]. | ||
| + | : 3. Water in the [[Reactor Core|reactor core]] becomes contaminated with [[radioactive]] [[material]] so the [[Heat Exchanger|heat exchanger]] heats up uncontaminated water. | ||
| + | : 3. The uncontaminated water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine. | ||
| + | : 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin. | ||
| + | : 5. The generator makes an electrical current. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Advantages==== | ||
| + | *Can work continuously. | ||
| + | *Power supply can be varied depending on demand. | ||
| + | *Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses. | ||
| + | *High energy density (1kg of Uranium can provide the same energy as 10,000kg of coal). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Disadvantages==== | ||
| + | *Cost of fuel. | ||
| + | *Difficult to safely dispose of nuclear waste. | ||
| + | *There is a small risk of meltdown. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
'''Nuclear Fuel''' is a [[radioactive]] [[material]] which can be used to generate electricty. | '''Nuclear Fuel''' is a [[radioactive]] [[material]] which can be used to generate electricty. | ||
Revision as of 12:00, 3 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Nuclear Fuel is a radioactive material which can be used to generate electricty.
About Nuclear Fuel
- Nuclear Fuel has energy in its nuclear potential energy store which can be easily transferred into its thermal energy store.
- The most common nuclear fuels are Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239.
- Nuclear Fuel transfers energy to the thermal energy store during a nuclear reaction.
- Nuclear Fuel is very dangerous because it is radioactive which causes harm to living organisms.:
- When nuclear fuel is used the waste products are still radioactive so they must be buried deep underground where they cannot harm living organisms.
Power
- Nuclear Fuel can be used to provide power by generating electricity that can be sent to houses and industry.
| A diagram of a coal power station. |
- 1. Nuclear Fuel undergoes a nuclear reaction in the reactor core.
- 2. Water in the reactor core is heated and passed through a heat exchanger.
- 3. Water in the reactor core becomes contaminated with radioactive material so the heat exchanger heats up uncontaminated water.
- 3. The uncontaminated water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can work continuously.
- Power supply can be varied depending on demand.
- Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses.
- High energy density (1kg of Uranium can provide the same energy as 10,000kg of coal).
Disadvantages
- Cost of fuel.
- Difficult to safely dispose of nuclear waste.
- There is a small risk of meltdown.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Nuclear Fuel is a radioactive material which can be used to generate electricty.
About Nuclear Fuel
- Nuclear Fuel has energy in its nuclear potential energy store which can be easily transferred into its thermal energy store.
- The most common nuclear fuels are Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239.
- Nuclear Fuel transfers energy to the thermal energy store during a nuclear reaction.
- Nuclear Fuel is very dangerous because it is radioactive which causes harm to living organisms.:
- When nuclear fuel is used the waste products are still radioactive so they must be buried deep underground where they cannot harm living organisms.
Power
- Nuclear Fuel can be used to provide power by generating electricity that can be sent to houses and industry.
- A Nuclear Power Station transfers energy from the chemical potential energy store of the Nuclear Fuel to our homes by electricity.
| A diagram of a coal power station. |
- 1. Nuclear Fuel undergoes a nuclear reaction in the reactor core.
- 2. Water in the reactor core is heated and passed through a heat exchanger.
- 3. Water in the reactor core becomes contaminated with radioactive material so the heat exchanger heats up uncontaminated water.
- 3. The uncontaminated water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Can work continuously.
- Power supply can be varied depending on demand.
- Few power stations needed to supply a large number of houses.
- High energy density (1kg of Uranium can provide the same energy as 10,000kg of coal).
Disadvantages
- Cost of fuel.
- Difficult to safely dispose of nuclear waste.
- There is a small risk of meltdown.