Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Work Done is the amount of energy transferred by the action of a force.
About Work Done
- Work Done is measured in Joules.
- Work Done can only be calculated for objects moving in the direction of the force.
Equation
Work Done = Force X Distance moved in the direction of the force \[ W = F \times d\] \[ W = Fd\]
- Work done is written with a capital W. Force is written with a capital F. Distance is written with a lower case d.
Example Calculations
| A person lifts a 40N box by a height of 1.2m. Calculate the work done by the person against gravity. | The brakes on a car apply a force of 10,000N. The car travels a distance of 15m braking. Calculate the work done by the brakes. | A person carries a 20N box along a horizontal path of 20m. |
|
Force = 40N Distance moved in the direction of the force = 1.2m \( W = Fd\) \( W = 40 \times 1.2\) \( W = 48J\) |
Force = 10,000N Distance moved in the direction of the force = 15m \( W = Fd\) \( W = 10,000 \times 15\) \( W = 15,000J\) |
Force = 40N Distance moved in the direction of the force = 0m \( W = Fd\) \( W = 20 \times 0\) \( W = 0J\) No work has been done because the movement is not in the direction of the force. The weight acts downwards but the movement was horizontal. |
Work Done by Deformation
- When an object is deformed, such as a spring being stretched, work is done to transfer energy into its Elastic Potential Energy Store.
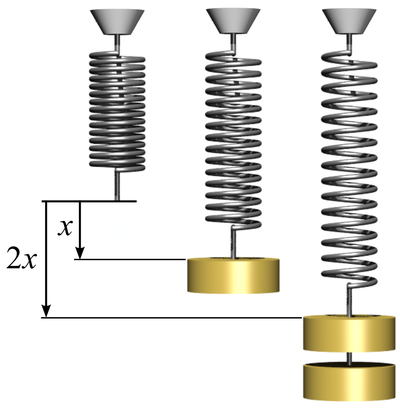
Work Done on a Spring
| Work is done to stretch this spring. |
- The Force needed to stretch a spring is proportional to the extension of the spring (Hooke's Law). Force = Spring Constant x Extension
- The Work Done on an object is proportional to the force and the distance traveled. Work Done = Force x Distance
- The distance moved is the same as the extension 'x'.
These two equations can be combined:
- 1. \( F = kx\)
- 2. \( W = Fx\)
Substitute 1 into 2. \[W = (kx) \times x\] \[W = kx^2\]