Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning

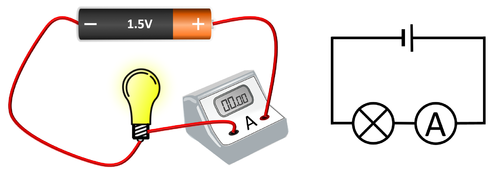
A picture showing an analogue ammeter.
An ammeter is a measuring device used to measure electrical current.
About Ammeters
- Ammeters are added in series to a circuit to find the current flowing through the circuit.
- An ideal ammeter has zero resistance because otherwise adding an ammeter to a circuit would change the current.
- Ammeters can be analogue with a needle pointing to numbers on a dial or it can be digital with a number display.
| An ammeter placed in series with a bulb. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An ammeter is a measuring device used to measure electrical current.
About Ammeters
- Ammeters are added in series to a circuit to find the current flowing through the circuit.
- An ideal ammeter has zero resistance because otherwise adding an ammeter to a circuit would change the current.
- Ammeters can be analogue with a needle pointing to numbers on a dial or it can be digital with a number display.
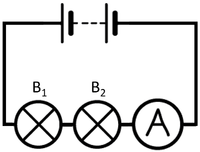
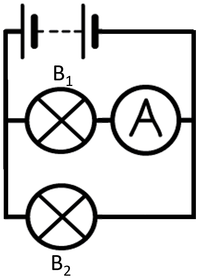
| To measure the current through bulb 1 the ammeter can be placed anywhere in this series circuit. | To measure the current through bulb 2 the ammeter can be placed anywhere in this series circuit. |
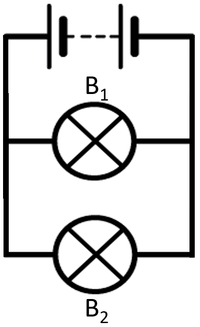
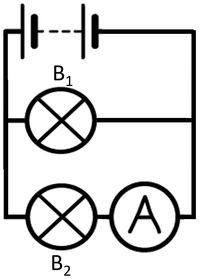
| To measure the current through bulb 1 the ammeter must be placed in series with bulb 1. | To measure the current through bulb 2 the ammeter must be placed in series with bulb 2. |
References
AQA
- Ammeter, pages 52-6, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA'
- Ammeters, page 41, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA'
- Ammeters, page 52, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA'
- Ammeters, pages 180, 239, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Ammeters, pages 25, 106, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Ammeters, pages 293, 296, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA'
- Ammeters, pages 60, 61, 235, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA'
- Ammeters, pages 62, 63, 331, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA'
- Ammeters; circuit symbol, page 38, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA'
Edexcel
- Ammeters, page 142, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Ammeters, page 382, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Ammeters, pages 186, 210, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Ammeters, pages 220, 338, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Ammeters, pages 73, 106, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel