Difference between revisions of "Chromatogram"
(→Key Stage 4) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
*Comparing the [[chromatogram]] of a [[sample]] to the [[chromatogram]]s of known [[chemical]]s. | *Comparing the [[chromatogram]] of a [[sample]] to the [[chromatogram]]s of known [[chemical]]s. | ||
*Calculating the [[Retention Factor|Retention Factor (R<sub>f</sub>)]] of the [[chemical]]s in the [[sample]] and comparing it to known [[Retention Factor|R<sub>f</sub>]] values. | *Calculating the [[Retention Factor|Retention Factor (R<sub>f</sub>)]] of the [[chemical]]s in the [[sample]] and comparing it to known [[Retention Factor|R<sub>f</sub>]] values. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Chromatograms, pages 182-183, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 3 November 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
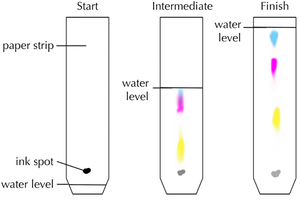
A chromatogram is the result of a chromatography experiment showing the relative distances moved by different chemicals in a sample.
About Chromatograms
Chromatograms can be used to identify chemicals in an unknown mixture by:
- Comparing the chromatogram of a sample to the chromatograms of known chemicals.
- Calculating the Retention Factor (Rf) of the chemicals in the sample and comparing it to known Rf values.