Difference between revisions of "Chromatogram"
(→About Chromatograms) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Chromatograms=== | ===About Chromatograms=== | ||
| − | [[Chromatogram]]s can be used to identify [[chemical]]s in an unknown [[mixture]] because different [[solute]]s [[diffusion|diffuse]] at different rates. | + | [[Chromatogram]]s can be used to identify [[chemical]]s in an unknown [[mixture]] because different [[solute]]s [[diffusion|diffuse]] at different rates. |
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:20, 23 February 2022
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
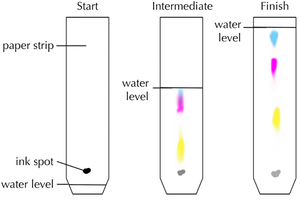
A chromatogram is the result of a chromatography experiment showing the relative distances moved by different chemicals in a sample.
About Chromatograms
Chromatograms can be used to identify chemicals in an unknown mixture because different solutes diffuse at different rates.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A chromatogram is the result of a chromatography experiment showing the relative distances moved by different chemicals in a sample.
About Chromatograms
Chromatograms can be used to identify chemicals in an unknown mixture by:
- Comparing the chromatogram of a sample to the chromatograms of known chemicals.
- Calculating the Retention Factor (Rf) of the chemicals in the sample and comparing it to known Rf values.
- Chromatography works because different solutes diffuse at different rates.
References
AQA
Edexcel
- Chromatogram, page 152, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Chromatogram, page 8, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Chromatograms, page 40, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Chromatograms, pages 108, 109, 111, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel