Key Stage 2
Meaning
Magnetism is a force that causes magnets to be attracted or repelled from one another.
- Noun: Magnetism
About Magnetism
- Magnetism is a non-contact force.
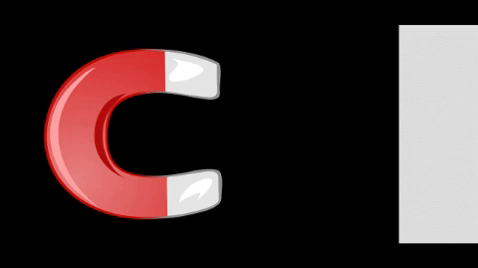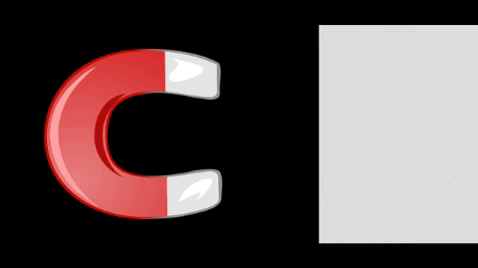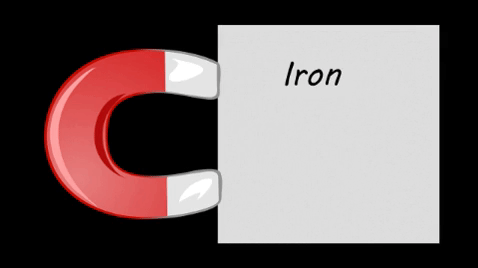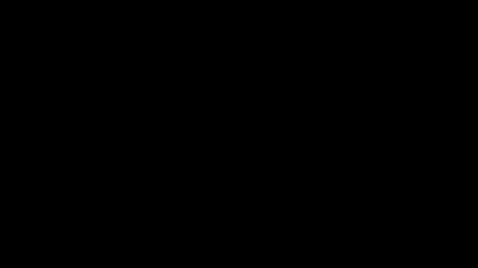
- Magnetism only affects certain materials:
- Magnetism can be attractive or repulsive.
|
|
| Two magnets facing North-North will repel each other and two magnets facing South-South will repel each other.
|
|
|
| Two magnets facing North-South will attract each other.
|
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Magnetism is a force that affects magnetic objects in a magnetic field.
About Magnetism
- Magnetism is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- Magnetism is a non-contact force because it can act without objects touching.
- Magnetism can be attractive when two opposite poles are near one another or repulsive when two 'like' poles are placed near one another.
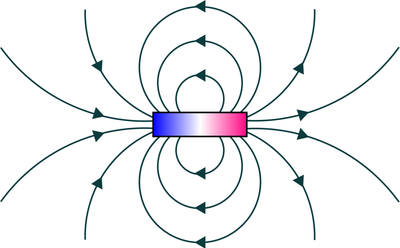
- Magnets produce a magnetic field. If Iron,Cobalt or Nickel are in that magnetic field they will be attracted to the magnet.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Magnetism is a force that affects magnetic objects in a magnetic field.
About Magnetism
- Magnetism is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- Magnetism is a non-contact force because it can act without objects touching.
- Magnetism can be attractive when two opposite poles are near one another or repulsive when two 'like' poles are placed near one another.
- Magnets produce a magnetic field. If Iron,Cobalt or Nickel are in that magnetic field they will be attracted to the magnet.
References
AQA
- Magnetic forces, page 119, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Magnetic forces, pages 209, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Magnetic forces, pages 216, 217, 221-224, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Magnetic forces, pages 289, 290, 295-298, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Magnetic forces, pages 92, 94, 95, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Magnetism, pages 214-231, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Magnetism, pages 216, 217, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Magnetism, pages 289, 290, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Magnetic forces, pages 172-173, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Magnetic forces, pages 406-407, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Magnetism, page 133, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Magnetism, page 375, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel