Key Stage 2
Meaning
A moon is a large rock which orbits a planet.
About Moons
- If it goes around a planet and it was not made by humans then it is called a moon.
- The Earth has one moon called The Moon.
- Some planets have no moons like Mercury and Venus.
- Some planets have many moons. Jupiter has 67 moons.
Examples
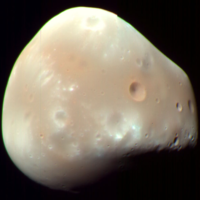
The two moons orbiting Mars.
| Phobos
|
Deimos
|
|
|
|
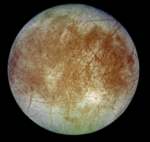
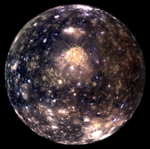
The four largest moons of Jupiter.
| Io
|
Europa
|
Callisto
|
Ganymede
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A moon is a large rock which orbits a planet.
About Moons
- Moons are natural satellites orbiting a planet.
- Most moons are too small to have enough gravity to become round. They can be asteroids that were captured into orbit by a planets gravity.
- Mercury and Venus do not have any moons. All other planets have one or more moons.
The two moons orbiting Mars.
| Phobos
|
Deimos
|
|
|
|
The four largest moons of Jupiter.
| Io
|
Europa
|
Callisto
|
Ganymede
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A moon is a large rock which orbits a planet.
About Moons
- Moons are natural satellites orbiting a planet.
- Most moons are too small to have enough gravity to become round. They can be asteroids that were captured into orbit by a planets gravity.
- Mercury and Venus do not have any moons. All other planets have one or more moons.
The two moons orbiting Mars.
| Phobos
|
Deimos
|
|
|
|
The four largest moons of Jupiter.
| Io
|
Europa
|
Callisto
|
Ganymede
|
|
|
|
|
|
References
AQA
- Moon, orbit of, page 250, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Moon, page 11, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Moon, pages 278-9, 290, 292, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Moons, page 101, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Moons, page 249, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Moons, page 320, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Moons, pages 275, 277, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
OCR
- Moons, pages 238, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR