Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A Parallel Circuit is an electrical circuit with two or more paths the current can flow along.
About Parallel Circuits
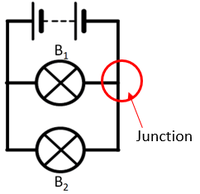
- In a parallel circuit the current is split at junctions before taking a different path.
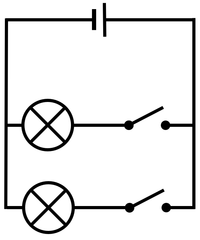
- Switches can be placed in a Parallel Circuit to allow current along one path at a time.
- Components placed in parallel with each other have the same Potential Difference across them.
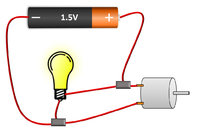
| The current from the battery splits at the junction sharing the current between the two bulbs. | The two bulbs in this parallel circuit can be switched on and off separately. |
Examples
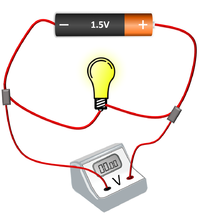
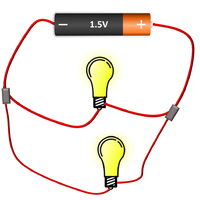
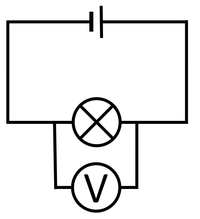
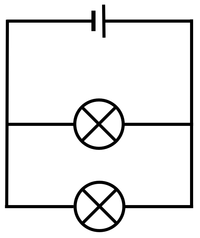
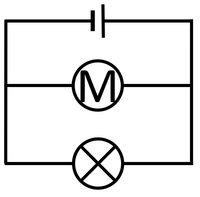
| The cell, bulb and voltmeter are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them. | The two bulbs are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. | The bulb and motor are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A Parallel Circuit is an electrical circuit with two or more paths the current can flow along.
About Parallel Circuits
- In a parallel circuit the current is split at junctions before taking a different path.
- Switches can be placed in a parallel circuit to allow current along one path at a time.
- Components placed in parallel with each other have the same potential difference across them.
| The current from the battery splits at the junction sharing the current between the two bulbs. | The two bulbs in this parallel circuit can be switched on and off separately. |
Examples
| The cell, bulb and voltmeter are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them. | The two bulbs are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. | The bulb and motor are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. |
Resistors in Parallel
NB: You only need to know what happens with identical resistors in parallel.
- When identical resistors are added in parallel there are more paths for the electricity so the resistance is reduced.
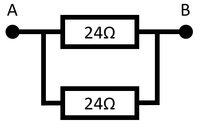
| Two identical resistors in parallel gives twice the number of paths, so has half the resistance.
The resistance between points A and B is 12Ω. |
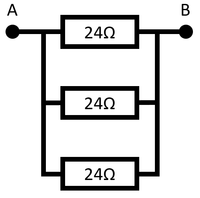
Three identical resistors in parallel gives three times the number of paths, so has a third of the resistance.
The resistance between points A and B is 8Ω. |
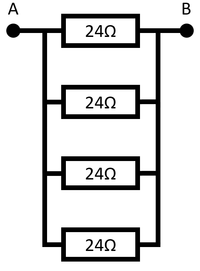
Four identical resistors in parallel gives four times the number of paths, so has a quarter of the resistance.
The resistance between points A and B is 6Ω. |
References
AQA
- Parallel circuit, pages 54-5, 62-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Parallel circuits, page 29, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, page 302, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 186, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 29, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 37, 47, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 60-61, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 72-76, 78, 79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 74-78, 80, 81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Parallel circuits, page 141, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Parallel circuits, page 75, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Parallel circuits, pages 188, 189, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Parallel circuits, pages 235-238, 240, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Parallel circuits; resistors, page 147, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel