Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A permanent magnet is an object with its own magnetic field that remains there even when there are no other external magnetic fields.
About Permanent Magnets
- A bar magnet is a permanent magnet.
- Permanent magnets are used in a electrical motors.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A permanent magnet is an object with its own magnetic field that remains there even when there are no other external magnetic fields.
About Permanent Magnets
- A bar magnet is a permanent magnet.
- Permanent magnets are used in a electrical motors.
- A magnet is made of several small magnetic domains which are regions in the magnet which act as smaller magnets. In a permanent magnet these magnetic domains are fixed in place and need energy to change their magnetic direction.
- A permanent magnet can only lose its magnetic field under certain conditions:
- When it is struck with a sudden force.
- When it is heated.
- When an extremely strong external magnetic field is applied.
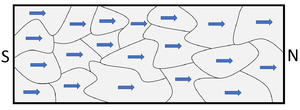
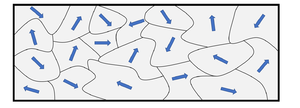
| When magnetic domains are aligned the object has its own magnetic field so it acts like a magnet. | When the magnetic domains are not aligned it does not have a magnetic field because the effect of the magnetic domains cancels out. |
References
AQA
- Permanent magnet, pages 242, 245, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Permanent magnets, page 223, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Permanent magnets, page 229, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Permanent magnets, page 92, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Permanent magnets, pages 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Permanent magnets, page 168, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Permanent magnets, page 267, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel