Difference between revisions of "Stopping Distance"
(→About Stopping Distance) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
**The conditions of the road and tyres - The less [[friction]] between the road and tyres the longer the [[Braking Distance|braking distance]] and therefore '''stopping distance'''. | **The conditions of the road and tyres - The less [[friction]] between the road and tyres the longer the [[Braking Distance|braking distance]] and therefore '''stopping distance'''. | ||
**The condition of the brakes, if they are in poor condition there will not be enough [[friction]]. | **The condition of the brakes, if they are in poor condition there will not be enough [[friction]]. | ||
| − | **The [[mass]] of the car. The mass a car has the more [[force]] is required to slow it down so brakes providing a constant [[force]] won't be as effective. ''Higher: See [[Inertial Mass]]''. | + | **The [[mass]] of the car. The more [[mass]] a car has the more [[force]] is required to slow it down ([[Newton's Second Law]]) so brakes providing a constant [[force]] won't be as effective. ''Higher: See [[Inertial Mass]]''. |
**[[Weather]] conditions - Ice reduces friction with the road making braking distance longer. | **[[Weather]] conditions - Ice reduces friction with the road making braking distance longer. | ||
Revision as of 09:06, 20 October 2020
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Stopping distance is the distance a vehicle travels between the driver noticing a hazard and coming to a stop.
About Stopping Distance
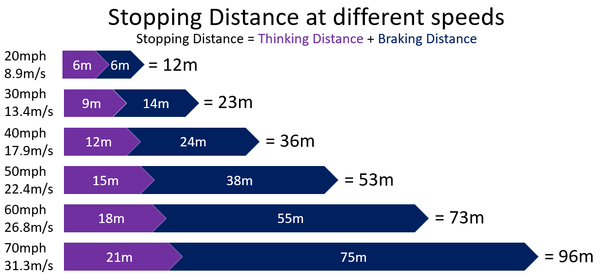
Stopping distance is made of two parts:
- Thinking Distance - The distance travelled by the vehicle between noticing a hazard and putting the foot on the brakes.
- Braking Distance - The distance travelled once the vehicle has applied the brakes.
Stopping Distance = Thinking Distance + Braking Distance
Stopping distance depends on:
- The speed of the vehicle - The greater the speed the larger the stopping distance.
- Thinking Distance
- The reaction time of the driver - The longer the reaction time the longer the thinking distance. This is affected by alcohol, drugs and tiredness.
- Braking Distance
- The conditions of the road and tyres - The less friction between the road and tyres the longer the braking distance and therefore stopping distance.
- The condition of the brakes, if they are in poor condition there will not be enough friction.
- The mass of the car. The more mass a car has the more force is required to slow it down (Newton's Second Law) so brakes providing a constant force won't be as effective. Higher: See Inertial Mass.
- Weather conditions - Ice reduces friction with the road making braking distance longer.
References
AQA
- Stopping distance, page 164, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Stopping distance, pages 141, 166-7, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Stopping distance, pages 242, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Stopping distances, pages 148-149, 157, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Stopping distances, pages 176-178, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Stopping distances, pages 208-210, 212, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Stopping distances, pages 215, 216, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Stopping distances, pages 67, 69, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Stopping distances, page 155, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Stopping distances, page 22, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Stopping distances, pages 26-27, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Stopping distances, pages 49-52, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Stopping distances; estimating, page 51, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Stopping distances; factors affecting, pages 49, 50, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Stopping distances; typical values, page 52, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel