Key Stage 3
Meaning
A wave is a vibration that transfers energy from one location to another.
About Waves
- Waves can transmit energy and information from one place to another.
- Waves travel through a medium that allows the vibration.
When a wave meets a boundary between two materials it can be:
- There are two types of wave; transverse and longitudinal.
- In longitudinal waves the vibration is in the same direction as the energy transfer.
- In transverse waves the vibration is perpendicular to the direction as the energy transfer.
Examples
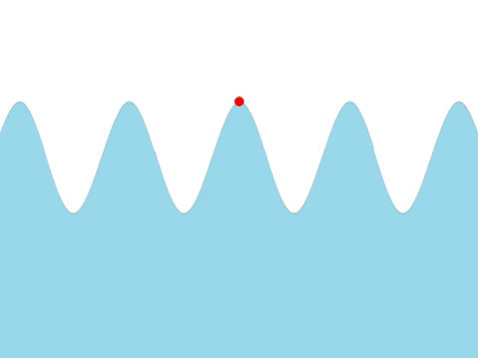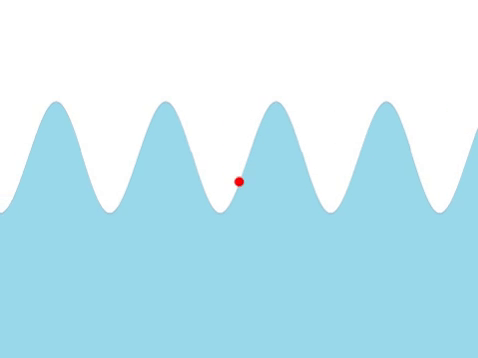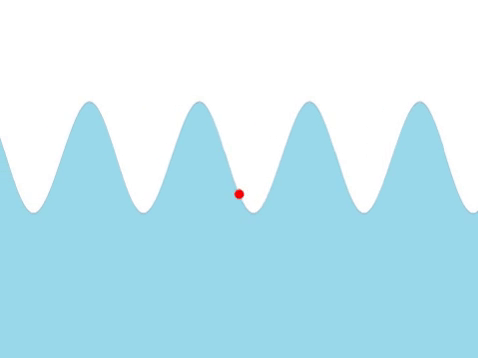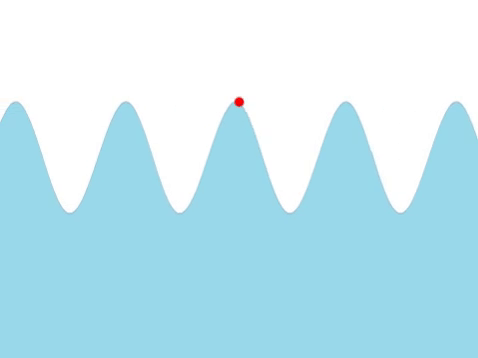
| Water Waves
|
|
|
| A water wave appears as a transverse from the surface.
|
| Sound Waves
|
|
|
| Sound waves are longitudinal waves of compression.
|
References
AQA
- Waves, page 181, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Waves, page 219, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Waves, pages 187-190, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Waves, pages 190-237, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Waves, pages 224-227, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Waves, pages 73-90, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA