Difference between revisions of "Wave Power"
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
*Unreliable because they are dependent on wind. | *Unreliable because they are dependent on wind. | ||
*Damages the habitats of sea creatures. | *Damages the habitats of sea creatures. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10424 ''Wave power, page 177, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac498 ''Wave power, page 20, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Wave power, page 38, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Wave power, pages 32-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Wave power, pages 50, 51, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Wave power, pages 52, 53, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:12, 14 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Wave Power is an energy resource that uses the movement of waves on the water to generate electricity.
About Wave Power
- Wave Power is a renewable energy resource.
- Wave Power has energy in the kinetic energy store of water waves.
Power
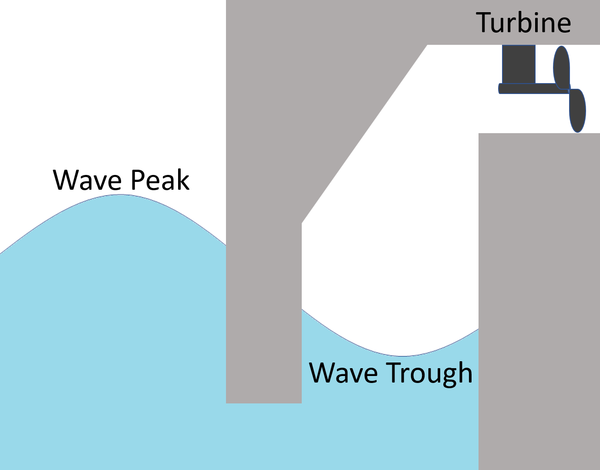
Wave Power can be used to generate electricity.
| A diagram of a wave generator. |
- 1. Water rises and falls inside a chamber due to the waves.
- 2. The water forces air to rush in and out of a chamber through pipes.
- 3. The air turns a turbine.
- 4. The turbine turns a generator.
Advantages
- Do not produce pollution.
- No fuel costs.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Require many of them to generate meaningful amounts of power.
- Can only be built on the coast.
- Hazardous to boats.
- Unreliable because they are dependent on wind.
- Damages the habitats of sea creatures.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Wave Power is an energy resource that uses the movement of waves on the water to generate electricity.
About Wave Power
- Wave Power is a renewable energy resource.
- Wave Power has energy in the kinetic energy store of water waves.
Power
Wave Power can be used to generate electricity.
| A diagram of a wave generator. |
- 1. Water rises and falls inside a chamber due to the waves.
- 2. The water forces air to rush in and out of a chamber through pipes.
- 3. The air turns a turbine.
- 4. The turbine turns a generator.
Advantages
- Do not produce pollution.
- No fuel costs.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build.
- Require many of them to generate meaningful amounts of power.
- Can only be built on the coast.
- Hazardous to boats.
- Unreliable because they are dependent on wind.
- Damages the habitats of sea creatures.
References
AQA
- Wave power, page 177, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Wave power, page 20, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Wave power, page 38, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Wave power, pages 32-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Wave power, pages 50, 51, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Wave power, pages 52, 53, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA