Anaerobic Respiration
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Anaerobic Respiration is the process of releasing stored chemical energy from sugars by breaking them down without Oxygen present.
About Aerobic Respiration
- Anaerobic respiration can take place in different ways in animal cells, plant cells and bacteria some producing Lactic Acid and others producing ethanol.
- In yeast anaerobic respiration produces ethanol which is Alcohol (Drug).
- When bacteria or yeast use anaerobic respiration in food it is called fermentation.
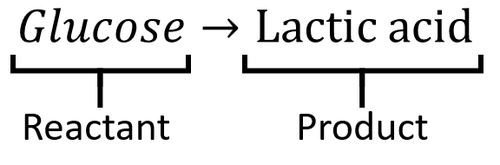
Word Equation
| A word equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells, plant cells and bacteria showing the reactants and products. |
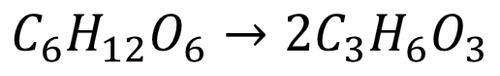
Symbol Equation
| A balanced symbol equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells and plant cells and bacteria. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Anaerobic Respiration is the process of releasing stored chemical energy from glucose in the absence of Oxygen.
About Anaerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration takes place in the muscles when they do not get enough Oxygen.
- Anaerobic respiration provides cells with the energy they need for protein synthesis, active transport and movement.
- In eukarytotic cells anaerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria.
- In prokaryotic cells anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Anaerobic respiration can take place in different ways in animal cells, plant cells and bacteria some producing Lactic Acid and others producing ethanol.
- In yeast anaerobic respiration produces ethanol which is Alcohol (Drug).
- When bacteria or yeast use anaerobic respiration in food it is called fermentation.
Chemical Equations
Anaerobic Respiration: (in humans): Glucose → Lactic Acid
Anaerobic Respiration: (in humans): C6H12O6 → 2C3H6O3
Anaerobic Respiration: (in yeast): Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
Anaerobic Respiration: (in yeast): C6H12O6 → 2CH3CH2OH + 2CO2
References
AQA
- Anaerobic respiration, page 54, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, page 62, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 108-10, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 12, 38-39, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 123-5, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 138-139, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 161, 162, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 175, 176, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration; in plants, page 162, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration; in plants, page 176, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration; in yeast, page 162, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA'
- Anaerobic respiration; in yeast, page 176, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA'
Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration, page 112, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration, page 162, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration, page 177, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration, page 64, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration, page 92, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration, pages 271, 272, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Anaerobic respiration; exercise, page 119, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel